What Is Potting Material for Electronic Components
What Is Potting Material for Electronic Components
Potting compound is essential for shielding delicate and mission-critical electronic bits from hazard. In even the toughest of exploring circumstances, it offers much-desired protection – not just by boosting mechanical fortitude but also by amplifying electrical insulation.
From consumer electronics to aerospace, automotive, and other companies where electronical hardware features largely, potting compounds are ubiquitous!

What is Potting Material for Electronic Components?
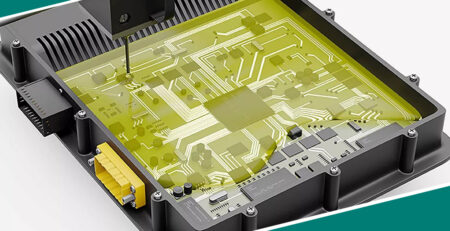
Ever opened up an electronic device only to find the entire board or casing totally encased in some type of hard epoxy? Yeah, that’s what electrical potting compound is – a sticky resin used to envelop electronics and protect them from whatever environment they may end up in.
Depending on the purpose or need for protection, there are various compounds available with slightly different properties. So, when it is time to arm your high-tech devices against Mother Nature – electrical potting compounds got you covered!
The Variety of Potting Materials for Electronic Components
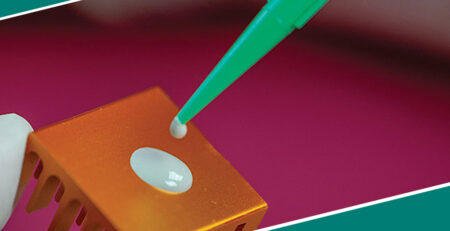
Protection is key, which makes potting compounds essential – and their materials depend on what’s being protected. Take urethane (or polyurethane) for instance: these electronic-potting babies can take the heat, skyrocketing up to 120°C. That’s why they’re perfect for super-durable circuits or outdoor power supplies that face extreme weather conditions.
On the flip side, silicone electrical potting compounds can come in handy for protecting lights from ultraviolet rays and keeping their color vivid. But you have to be sure you get the right kind – some generate heat during curing and might even cause harm to certain ICs, not to mention that once it’s on there, there is no going back.
What is The Use of Potting Materials?
As I previously mentioned, the potting compound creates a safe haven for electronics, enabling them to exchange air while still being protected from potentially detrimental environmental hazards like heat and corrosion. Moreover, it can even add some extra time onto an item’s shelf life!
Transformers are the way to go if you’re looking for an electrical potting compound as they’ve got some pretty convenient features; their heat levels and extra insulation from magnetic and electrical fields make them a much more reliable application. Plus, with that foil wrap you get, you don’t have to worry about something going wrong!
What is The Chemistry of Potting Materials?
No doubt, electronic potting comes in three major types: epoxy resins, silicones and urethane-based (polyurethanes or PU). Each type of potting has its own unique applications and benefits. But before getting into the specifics of each compound, there is one thing to bear in mind – these substances are made up of potent chemicals which can endure time as well as extreme conditions.
Thus, it should come as no surprise that handling them requires specialized apparatus and regulated settings – particularly when it comes to resin curing processes which generate byproducts like gas fumes!
A Summary of The PCB Potting Process
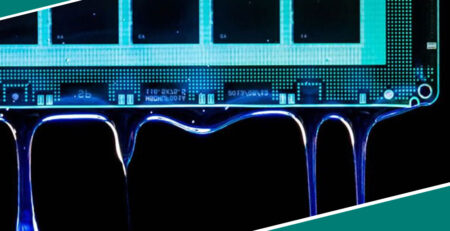
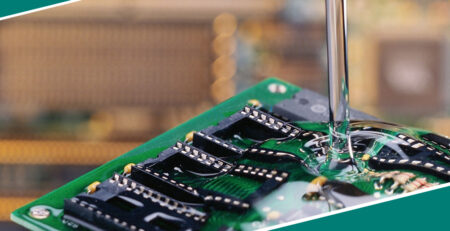
It’s essential for a successful potting of PCBs to house the board in a certain casing, known as the ‘potting box’. All you have to do is fill it with an electrical compound until it meets required levels.
The curing phase can take as little as minutes (depending on base materials) till the compound hardens, protecting your case and PCB innately. A cost-effective alternative usually used are non-epoxy reactive plastic cases: quick and simple to install.
How is Potting Different from Encapsulation?
Potting doesn’t absolutely have to be a process in which the PCB is fully covered – for some tasks, potting can be specialized to pour over particular components; that’s called PCB encapsulation.
Noting that when it comes to “potting” – think of it as having both a case surrounding an element with the compound sealing it off without being taken apart. Encapsulation takes this concept one step further, factoring in the removal of resin/board body from its container afterward.
What is The Best Potting Material for Electronic Components?
Depending on the composition of the potting compound, its application and use will differ – as we already discussed. Epoxy resins are great for SMT applications due to their excellent chemical resistance and heat tolerance.
Talking about PU potting compounds, they are the real deal when it comes to low temp endurance and thermal cycling. As for silicone compounds, they are not too shabby either – great light endurance properties and still reliable under hot-cold fluctuations.
What’s The Duration of Potting Materials?
Temperature can be a tough measure for any potting compound’s durability – soft or silicone resins tend to hold up better over long-term thermal cycles, but the more durable epoxy-based resins could last almost a lifetime!
We’re talking up to 1500 cycles of major temperature shifts without losing their strength – that’s easily translated into years of dependable use in the field.
The Curing of Potting Takes How Long?
Depending on the type of resin used, curing time can range from a mere ten to thirty seconds for UV-based resins to up to fifteen minutes for epoxy potting compounds. Bear in mind though that some compounds may give off dangerous fumes and generate heat during this process – which is why it’s important to take the necessary safety precautions and design considerations into account prior to use.
Don’t forget either that preparing your chosen potting compound properly is key; you need just the right combination of resin elements with suitable dispensing speed and optimal application temperatures.
Is it Possible to Remove Potting Materials?
Depotting, or removing a protective potting compound, can vary greatly depending on the base material. For example, with hard resins, applying acetone and heat can dissolve parts of it – if it hasn’t cured yet.
However, if this is not an option due to the resin being already hardened, physical force may be used (but we don’t recommend you try!). Secondly there are dangerous chemicals that might work for depotting. Unless done in an appropriate environment however these hazardous materials will put both electronics components and yourself at risk so stay away!

Final Thoughts
In today’s world, electronics are absolutely everywhere, making huge improvements to folks’ lives in the form of tiny personal devices and larger automated industrial installations. To keep these delicate components safe from their ever-changing environment – from corrosive chemicals and dust particles to extreme temperatures and vibrations– potting compounds are vital.
For more about a complete guide to Potting Material for Electronic Components, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.