Metal Bonding Adhesive

In the realm of modern manufacturing and construction, the role of adhesive technology has become increasingly prominent, especially in the context of metal bonding. Metal bonding adhesives, known for their exceptional strength, durability, and versatility, have revolutionized the way industries approach joining and securing metal components. This article delves into the various aspects of metal bonding adhesives, highlighting their applications, advantages, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Metal Bonding Adhesive
Metal bonding adhesives are specialized adhesives designed to create solid, durable bonds between metal surfaces. These adhesives offer unique advantages over traditional mechanical fastening methods, such as welding or riveting, by providing a seamless, smooth finish without additional hardware. Understanding metal bonding adhesives is crucial for industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and construction, where joining metal components with precision and reliability is paramount. Key points to consider when delving into the realm of metal bonding adhesives include:
- Chemistry and Composition:Formulators design metal bonding adhesives to work with metal surfaces specifically. They often contain epoxy, acrylic, cyanoacrylate, or polyurethane resins that ensure excellent metal adhesion.
- Surface Preparation:Achieving a successful bond relies heavily on proper surface preparation. Metal surfaces should be thoroughly cleaned, degreased, and sometimes treated to enhance adhesion. One might employ sanding, chemical etching, or plasma treatment to create a microscopically rough surface that enhances adhesive contact.
- Adhesive Selection:Manufacturers tailor metal bonding adhesives for various metal types and applications. The choice of adhesive depends on factors such as load-bearing requirements, temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and curing time.
- Curing Mechanisms:Metal bonding adhesives typically cure through chemical reactions, heat, or UV light. Understanding the curing process is vital to ensure sufficient bond strength and stability.
- Bond Strength and Durability:Properly applied metal bonding adhesives can create bonds that exhibit exceptional strength and durability, often with a degree of flexibility to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction.
- Testing and Quality Control:Rigorous testing protocols are essential to verify the performance of metal bonded assemblies. Techniques like shear testing, peel testing, and aging tests assess bond strength and long-term stability.
- Application Techniques:Dispensing and applying metal bonding adhesives require precision. Techniques like manual application, automated dispensing, or even structural bonding with pre-cured adhesive films might be employed, depending on the scale and complexity of the project.
- Safety and Environment:Working with metal bonding adhesives demands attention to safety precautions, as some formulations can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during curing. Proper ventilation and protective gear are necessary.
Types of Metal Bonding Adhesives
Metal bonding adhesives play a crucial role in various industries, enabling joining of metals with strong, durable, and reliable bonds. Designers create these adhesives to deliver exceptional performance, enhancing structural integrity and reducing the reliance on traditional welding or mechanical fastening methods. There are several types of metal bonding adhesives, each offering unique properties and applications:
Epoxy Adhesives
- They are known for their excellent bonding strength and durability.
- Suitable for bonding a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper.
- Resistant to chemicals, temperature fluctuations, and moisture.
- The aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries use them.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives
- They are also called “super glues” for their rapid bonding capability.
- Ideal for bonding small metal parts quickly and securely.
- It offers good resistance to shear and impact forces.
- People commonly use them in jewelry making and electronics assembly.
Acrylic Adhesives
- Provide high strength and versatile bonding for various metals.
- Offer excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemicals.
- Available in different formulations, such as two-component structural adhesives.
- They find usage in signage, construction, and automotive applications.
Polyurethane Adhesives
- Flexible adhesives are suitable for metals with different expansion rates.
- Exhibit good impact resistance and high peel strength.
- They can absorb vibrations, making them ideal for applications subject to movement or stress.
- They find use in the automotive, construction, and electronics industries.
Anaerobic Adhesives
- Cure in the absence of air and the presence of metal ions.
- Ideal for thread locking and retaining applications in metal assemblies.
- Provide solid and vibration-resistant bonds.
- They see wide usage in manufacturing, maintenance, and repair.
Silicone Adhesives
- Excellent for high-temperature bonding applications.
- Maintain flexibility over a wide temperature range.
- Offer good electrical insulation properties.
- They find use in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
Modified Silane Adhesives
- Provide exceptional adhesion to metals, including stainless steel and aluminum.
- Resistant to extreme temperatures, moisture, and chemicals.
- They find use in applications involving structural bonding and sealing.
Advantages of Using Metal Bonding Adhesives
Metal bonding adhesives offer a range of remarkable advantages, making them a preferred choice for various industrial applications. These advanced adhesives possess unique qualities that enhance performance, durability, and efficiency in bonding metal substrates. Some key advantages of using metal bonding adhesives include the following:
- Strong and Durable Bonds:Metal bonding adhesives create potent bonds that distribute stress evenly across the bonded area, minimizing the risk of localized stress points and potential failure. This results in long-lasting and durable connections, even under challenging conditions.
- Versatility:Metal bonding adhesives are compatible with various metals, including steel, aluminum, copper, and even dissimilar metals. This versatility allows for more significant design and material selection flexibility while maintaining structural integrity.
- Corrosion Resistance:These adhesives can provide a barrier against moisture and other corrosive agents, preventing the formation of rust and corrosion that can weaken metal joints over time. This feature is especially crucial in outdoor or harsh environments.
- Reduced Weight:Unlike traditional mechanical fasteners, metal bonding adhesives distribute stress evenly across the bonded surfaces, eliminating the need for additional bulky hardware. This reduction in overall weight of the assembly can lead to improved fuel efficiency in transportation applications.”
- Enhanced Aesthetics:Metal bonding adhesives create smooth and seamless bonds without needing visible rivets or screws. This approach contributes to a cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing final product, which is especially important in industries such as automotive and electronics.
- Vibration Damping:Metal bonding adhesives possess excellent vibration-dampening properties, absorbing and dissipating energy from machinery or other vibration sources. This mechanism helps to prevent fatigue-related failures and extends the lifespan of bonded components.
- Improved Stress Distribution:These adhesives can quickly bond to irregularly shaped or uneven surfaces. They fill gaps and imperfections, improving stress distribution and a stronger connection.
- Cost Efficiency:While the initial cost of metal bonding adhesives might be higher compared to traditional fasteners, the long-term benefits they offer in terms of reduced maintenance, improved product lifespan, and simplified assembly processes can lead to significant cost savings over time.
Key Considerations in Adhesive Selection
Selecting the appropriate adhesive is a critical decision that significantly influences the success and performance of metal bonding applications. To ensure optimal adhesive selection, one must take into account several key considerations:
- Substrate Compatibility:One of the primary considerations involves evaluating the adhesive’s compatibility with the specific types of metal substrates that undergo bonding. Different metals have varying surface properties and chemical compositions that can impact adhesive adhesion and performance.
- Bond Strength Requirements:One must assess the intended load-bearing capacity of the bonded joint. Adhesives come with different strength levels, and choosing the suitable adhesive with appropriate shear, tensile, and peel strengths is essential to meet the mechanical demands of the application.
- Environmental Conditions: The operating environment, including temperature variations, humidity, exposure to chemicals, and UV radiation, plays a significant role in adhesive performance. Choosing an adhesive with the appropriate resistance to these conditions ensures the longevity of the bond.
- Curing Time and Process:Adhesives require specific curing times and conditions for optimal bonding strength. It’s crucial to consider the available curing methods—whether room temperature, heat, or UV—and match them with the production timeline and process feasibility.
- Gap Filling and Surface Preparation:Evaluate the adhesive’s ability to fill gaps and adhere to irregular surfaces. The surface may require preparation, such as cleaning, sanding, or using primers, to enhance adhesive bonding.
- Thermal Expansion Compatibility:Metals have different coefficients of thermal expansion, which can lead to stress and potential failure if not addressed. Choosing an adhesive with similar thermal expansion properties to the metal substrates helps mitigate these issues.
- Ease of Application:Consider the adhesive’s ease of handling and application. Some adhesives require precise mixing ratios, while others come in pre-mixed forms. The easy application can reduce the risk of errors during the bonding process.
- Regulatory and Health Considerations:Adhesives may have specific regulatory requirements based on their intended application, such as food-contact regulations or environmental standards. Health and safety considerations for users during adhesive application and curing are also important.
- Long-Term Durability and Aging:Assess the adhesive’s resistance to aging, including creep, fatigue, and long-term structural stability. Adhesives that maintain their properties over extended periods ensure the reliability of the bonded assembly.
Surface Preparation for Effective Bonding
Surface Preparation for Effective Bonding is crucial for achieving robust and reliable metal bonding using adhesives. Proper surface preparation ensures that the adhesive can create a durable and long-lasting bond between metal surfaces. Here are some key points to consider for adequate surface preparation:
- Cleanliness is Key: Before applying any adhesive, thoroughly clean the metal surfaces to remove dirt, dust, grease, oil, and contaminants that might hinder proper bonding. You can use solvents, degreasers, or cleaning solutions for this purpose.
- Degreasing: Grease and oils can create a barrier that prevents adhesives from directly contacting the metal surface. Degreasing using suitable solvents is essential to remove these substances and ensure a clean surface.
- Mechanical Abrasion:You can mechanically rub the metal surface to enhance the adhesive’s bondability. This process roughens the surface, creating more surface area for the adhesive to adhere to. Depending on the metal type and adhesive used, techniques like sanding, grit blasting, or grinding can be employed.
- Etching:Some metals, such as aluminum and stainless steel, benefit from etching to create a microscopically rough surface. This process improves adhesion by providing a more textured surface for the adhesive to grip.
- Surface Activation:Certain metals, like aluminum, tend to form oxide layers that can hinder bonding. Surface activation methods, such as chemical or plasma treatments, can modify the metal’s surface chemistry, improving adhesive bonding.
- Priming:Using a suitable primer can further enhance bonding. Primers create a chemical bridge between the metal and adhesive, promoting better adhesion and increasing the overall bond strength.
- Choosing the Right Adhesive:Different adhesives work better with specific surface preparation techniques and types of metals. Matching the adhesive tape to the metal and surface condition is critical for successful bonding.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Recommendations:Adhesive manufacturers often provide guidelines for surface preparation specific to their products. You should follow these recommendations closely to ensure optimal bonding results.
- Avoid Contamination:After preparing the surface, handling the metal parts with clean gloves is essential to prevent any oils or contaminants from being transferred back onto the surface.
Adhesion Mechanisms in Metal Bonding
Adhesion mechanisms are pivotal in metal bonding adhesives, facilitating solid and durable connections between metal surfaces. These mechanisms encompass a range of interactions at the molecular level that contribute to the adhesive’s effectiveness. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for designing and selecting suitable adhesives for specific applications. Several vital points elucidate the adhesion mechanisms in metal bonding:
- Chemical Bonding:Adhesives can form chemical bonds with metal surfaces through covalent bonding, where atoms are shared between the adhesive and the metal, enhancing the overall strength of the connection.
- Physical Interlocking:Microscopic irregularities on metal surfaces allow for physical interlocking between the adhesive and the metal, creating mechanical adhesion. This interlocking increases the contact area, leading to improved bond strength.
- Electrostatic Interactions:Electrostatic forces can attract adhesive molecules to metal surfaces, mainly when charged or polar groups are present in the adhesive and the metal.
- Van der Waals Forces: These weak forces arise due to temporary fluctuations in electron density, leading to attractive interactions between adhesive and metal molecules. Although individually weak, these forces can collectively contribute to adhesion.
- Surface Energy Matching:Adhesives with similar surface energy to the metal tend to spread more effectively, ensuring better wetting and coverage of the metal surface and enhancing adhesion.
- Chemisorption:Certain adhesive formulations contain molecules that chemisorb onto the metal surface, forming covalent solid bonds and promoting adhesion.
- Priming and Surface Treatment:Preparing metal surfaces through methods like sanding, acid etching, or applying primers can modify the surface properties, making them more receptive to adhesives by increasing surface area or introducing functional groups.
- Hydrogen Bonding:Functional groups like hydroxyl (OH) or amine (NH2) on adhesive molecules can form hydrogen bonds with metal surfaces, increasing adhesion.
- Thermosetting Adhesives:These adhesives undergo a chemical reaction upon curing, forming a three-dimensional network that tightly binds the metal surfaces together.
- Thermoplastic Adhesives:These adhesives soften when heated and solidify upon cooling. They create bonds through the diffusion of adhesive molecules into the metal surface.
Industrial Applications of Metal Bonding Adhesives
Metal bonding adhesives have revolutionized various industries by providing efficient and reliable alternatives to traditional mechanical fastening methods. These adhesives offer strong, durable, versatile bonding solutions for multiple applications, enabling enhanced performance and cost-effective manufacturing processes.
Automotive Industry
1.Structural Assembly:The automotive sector uses metal bonding adhesives to bond various components, including body panels, roofs, and chassis. They distribute stress evenly, reducing the need for welding or riveting and improving crash resistance and overall vehicle strength.
2.Vibration Dampening:Adhesives help dampen vibrations and noise, contributing to a smoother and quieter ride. This quality is precious in electric vehicles, where noise reduction is essential due to the absence of traditional engine noise.
Electronics and Aerospace
- Miniaturization:In the electronics industry, metal bonding adhesives enable the miniaturization of devices by securely bonding delicate components to metal substrates without adding excess weight. Crucially, this factor contributes to the development of compact and lightweight gadgets.
- Aircraft Construction:Aerospace applications benefit from these adhesives as they provide lightweight and robust bonding solutions for joining metal panels and structures in aircraft. The adhesive’s ability to distribute loads evenly enhances fuel efficiency and reduces maintenance requirements.
Construction and Infrastructure
- Facade Panels:In construction, metal bonding adhesives attach metal facade panels to buildings. The adhesive’s weather resistance and durability ensure long-lasting and visually appealing exteriors.
- HVAC Systems:Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems utilize metal bonding adhesives to secure ductwork and joints. The adhesive’s thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer.
Medical Devices
- Surgical Instruments:Metal bonding adhesives are used in the medical field to bond metal components in surgical instruments. These adhesives’ biocompatibility ensures their safe use within the human body.
- Diagnostic Equipment:Medical diagnostic devices benefit from metal bonding adhesives’ precision and stability, allowing for the secure assembly of intricate components.
Energy Sector
- Renewable Energy Systems:Metal bonding adhesives play a role in assembling solar panels and wind turbines. Their resistance to environmental factors helps maintain the structural integrity of these systems over time.
- Battery Manufacturing:In energy storage, metal bonding adhesives contribute to the assembly of batteries, ensuring secure connections between metal components within battery cells.
Automotive Sector: Enhancing Structural Integrity
The automotive sector has witnessed a transformative shift in its manufacturing processes with the advent of metal bonding adhesives. These innovative adhesives have emerged as a game-changer, offering unparalleled benefits over traditional mechanical fastening methods. By enhancing structural integrity and overall vehicle performance, metal bonding adhesives have revolutionized how cars are designed, assembled, and driven.
Benefits and Applications
- Strength and Durability:Metal bonding adhesives provide a high-strength bond that distributes stress evenly across joints. Implementing this approach reduces stress concentrations and enhances the vehicle’s overall structural integrity, improving crash resistance and occupant safety.
- Weight Reduction:Unlike traditional welding or riveting methods, metal bonding adhesives reduce weight by eliminating the need for additional fasteners. As a result, we achieve improved fuel efficiency and reduced carbon emissions.
- Design Freedom:Adhesives enable manufacturers to explore innovative design options by bonding dissimilar materials and complex shapes. This flexibility leads to more aerodynamic and aesthetically pleasing vehicle designs.
- Vibration Dampening:Metal bonding adhesives absorb and dampen vibrations, leading to a smoother and quieter ride for passengers. This characteristic is precious in electric vehicles, where noise reduction is a key feature.
Structural Assembly and Beyond
- Chassis and Body Panels:Manufacturers extensively use metal bonding adhesives to bond structural components such as chassis and body panels. The adhesive’s ability to bond metals of different compositions provides a cohesive and robust assembly, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Doors and Roofs:Adhesives contribute to the seamless bonding of doors and roofs, creating a unified and monolithic structure. These effects include enhanced aesthetics, reduced wind noise, and improved overall aerodynamics of the vehicle.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):The lightweight nature of metal bonding adhesives is particularly advantageous in EVs, where battery weight can impact range. Adhesives assist in the secure attachment of battery packs and other components.
Future Implications
The automotive industry’s adoption of metal bonding adhesives is poised to continue its upward trajectory. As electric and autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, the demand for lightweight materials and advanced bonding solutions will rise. Manufacturers will further explore innovative adhesive formulations to enhance heat resistance for EVs and optimize crash performance for autonomous vehicles.
Aerospace Industry: Lightweight Bonding Solutions
In the dynamic landscape of the aerospace industry, the pursuit of efficiency and performance reigns supreme. As aircraft design evolves to prioritize lightweight structures for improved fuel efficiency and maneuverability, advanced bonding solutions, particularly metal bonding adhesives, become increasingly vital. These innovative bonding technologies create solid and durable connections while minimizing the overall weight of aerospace components.
Advantages of Metal Bonding Adhesives
- Weight Reduction:Traditional mechanical fasteners add considerable weight to aerospace assemblies. Metal bonding adhesives offer a lightweight alternative, allowing engineers to trim excess weight without compromising structural integrity.
- Enhanced Structural Integrity:Metal bonding adhesives form a uniform distribution of stress across the bonded surfaces, reducing stress concentrations standard with traditional fasteners. This results in enhanced structural integrity and resistance to fatigue, which is vital for the rigorous demands of aerospace applications.
- Design Flexibility:Adhesives provide greater design freedom by enabling the bonding of dissimilar materials and complex geometries. This flexibility facilitates innovative design approaches that can optimize aerodynamics and overall performance.
Challenges and Solutions
- Extreme Conditions:Aerospace components operate in various conditions, from freezing altitudes to scorching heat. Engineers develop metal bonding adhesives for the aerospace industry to withstand these extremes, ensuring longevity and reliability.
- Vibration and Shock: Aircraft experience continuous vibration and shocks during flight. Formulators design metal bonding adhesives to absorb and dampen these vibrations, reducing material fatigue and failure risk.
- Surface Preparation:Achieving a solid bond requires meticulous surface preparation. Aerospace-grade metal bonding adhesives often include primers that improve adhesion to metals and provide corrosion protection.
Innovations and Future Directions
- Nanotechnology Integration:Ongoing research explores the integration of nanomaterials within adhesives to enhance further their mechanical properties, thermal resistance, and durability.
- Self-Healing Adhesives:Scientists are investigating self-healing adhesive technologies that can repair minor damages to the bond line, extending the lifespan of aerospace components and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Intelligent Monitoring:Integrating sensors within adhesive joints is being explored to enable real-time structural health monitoring. This technology could revolutionize maintenance practices by providing early warnings of potential failures.
Construction and Architecture: Bonding Metal Elements
In the dynamic realm of construction and architecture, where innovation constantly reshapes design and structural integrity possibilities, the advent of metal bonding adhesives has ushered in a new era of joining metal elements. Fortified by cutting-edge technologies, these adhesives offer a seamless alternative to traditional welding and mechanical fastening methods. A remarkable synergy of strength, flexibility, and aesthetics, they play a pivotal role in uniting metal components, enabling architects and engineers to craft structures that stand as a testament to form and function.
Key Advantages
- Enhanced Structural Integrity:Metal bonding adhesives provide high-strength bonding, distributing stress evenly across surfaces. This approach boosts structural robustness by minimizing weak areas, increasing load-bearing capacity, and improving overall structural strength.
- Design Flexibility:Unlike conventional welding, adhesive bonding allows for more intricate and complex designs. The absence of visible welds or fasteners enables architects to explore bold, seamless aesthetics emphasizing clean lines and uncluttered surfaces.
- Vibration Dampening:Metal adhesives absorb vibrations and distribute energy throughout the bonded area, reducing the transmission of vibrations across structures, which is especially important in buildings located in earthquake-prone regions.
- Corrosion Prevention:These adhesives create a barrier between metal surfaces, preventing direct contact and subsequently inhibiting the formation of corrosion. By extending the lifespan of structures, it also helps to reduce the need for maintenance requirements.
- Thermal Expansion Compatibility:Metal elements expand and contract with temperature changes. Metal bonding adhesives accommodate these fluctuations, ensuring a stable and durable bond over time.
- Time and Cost Efficiency:The adhesive application process is generally quicker than traditional methods, reducing labor costs and project timelines. Additionally, there’s no need for post-bonding treatments like grinding or finishing.
Applications
- Facade Cladding:Metal adhesives facilitate the secure attachment of metal panels to building exteriors, allowing for visually striking facades with a sleek, uninterrupted surface.
- Interior Elements:They enable the seamless integration of metal components in interior design, such as decorative panels, handrails, and staircases, achieving a modern and cohesive aesthetic.
- Structural Connections:Metal bonding adhesives can replace or complement traditional welding in connecting load-bearing structural elements, promoting efficiency and longevity.
- Renovation and Restoration:In historic building preservation, these adhesives enable the repair and replacement of metal ornaments and fixtures while preserving the authentic appearance of the structure.
Electronics Manufacturing: Precision Bonding Needs
In Electronics Manufacturing, achieving precision bonding is paramount to ensure the reliability and functionality of electronic devices. The bonding process involves creating a secure and lasting connection between different components, and when it comes to bonding metal components, the role of metal bonding adhesives becomes indispensable. Due to their unique properties and capabilities, these adhesives have emerged as versatile solutions for various electronic applications. Here’s a closer look at the significance of precision bonding and the role of metal bonding adhesives:

- Reliable Connections:Precision bonding is crucial to establish reliable electrical connections and mechanical stability in electronic devices. Metal bonding adhesives facilitate the creation of strong and durable bonds between metal surfaces, ensuring consistent performance and longevity.
- Challenges in Metal Bonding:Bonding metal surfaces presents challenges due to different thermal expansion coefficients and varying surface energies. Formulators create metal bonding adhesives to address these challenges, bridging the gap between dissimilar metals and compensating for their inherent differences.
- Material Compatibility:Designers create metal bonding adhesives for various metals, including aluminum, copper, stainless steel, and more. This versatility allows manufacturers to use the same adhesive for bonding different metal combinations, streamlining production processes.
- Adhesive Properties:These adhesives possess excellent adhesion strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. They can withstand the harsh conditions that electronic devices might encounter during their operational lifespan, ensuring the integrity of the bonded components.
- Conductive Adhesives:Conductive metal bonding adhesives offer a unique advantage in electronics manufacturing, where electrical connectivity is vital. These adhesives provide a strong bond and maintain electrical conductivity between bonded surfaces, eliminating the need for separate electrical pathways.
- Miniaturization and Flexibility:As electronics continue to shrink, the demand for precision in manufacturing grows. Metal bonding adhesives offer the flexibility to create intricate and miniaturized designs without compromising structural integrity.
- Cost and Efficiency:Metal bonding adhesives can reduce production costs compared to traditional methods like welding or soldering. They eliminate the need for extensive heat application, reducing energy consumption and the risk of heat-related damage.
Challenges in Metal Bonding Adhesive Applications
Metal bonding adhesives have revolutionized the way industries approach joining and assembling metal components. These versatile adhesives offer several benefits, including improved aesthetics, stress distribution, and corrosion resistance. However, like any technology, metal bonding adhesives come with challenges that manufacturers and engineers must address to ensure successful applications.
Substandard Surface Preparation
- Adhesive bonding success heavily relies on proper surface preparation.
- Metal surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned, degreased, and sometimes treated for optimal adhesion.
- Oils, oxides, and contaminants can hinder the adhesive’s ability to form a strong bond.
Diverse Metal Characteristics
- Different metals possess varying surface energies and reactivity.
- Selecting an adhesive compatible with specific metals is crucial.
- Dissimilar metal bonding can lead to galvanic corrosion, weakening the joint.
Thermal Expansion Mismatch
- Metals have distinct coefficients of thermal expansion.
- Temperature fluctuations can cause stress at the adhesive-metal interface.
- Improper bonding can lead to adhesive failure or shortened lifespan of the adhesive.
Mechanical Loads and Vibration
- Adhesive bonds are susceptible to peeling or shearing under mechanical stress.
- Proper adhesive selection and joint design are vital in applications involving vibrations or dynamic loads.
- We may require flexible adhesives to accommodate movement.
Curing and Processing
- Achieving consistent adhesive curing can be challenging.
- We must control factors such as temperature, humidity, and curing time.
- Improper curing can lead to weak bonds and reduced overall performance.
Harsh Environments and Corrosion
- Harsh chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures may expose metal bonding adhesives.
- Ensuring the adhesive’s resistance to corrosion and environmental stress is critical.
- Sealants or coatings may be necessary to protect the adhesive bond in such conditions.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
- Bonding metals to non-metallic materials adds complexity.
- We must choose adhesives with suitable adhesion properties for both materials.
- Differential expansion and contraction can challenge the bond’s integrity.
Quality Control and Testing
- Reliable bond quality requires stringent quality control measures.
- Non-destructive testing methods are crucial to ensure bond integrity.
- We should implement quality control procedures throughout the production process.
High-Temperature Resistance in Adhesive Bonds
Adhesive bonds play a pivotal role in joining metal components across various industries. However, when exposed to high temperatures, traditional adhesives often falter, weakening bonds and compromising structural integrity. The demand for adhesive bonds capable of withstanding extreme heat has spurred innovation in high-temperature resistance.
Importance of High-Temperature Resistance
- Many industrial applications, such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, involve elevated temperatures.
- Adhesive bonds must maintain strength and stability even when exposed to extreme heat.
Challenges in High-Temperature Environments
- Conventional adhesives often soften, degrade, or lose bonding strength at high temperatures.
- Thermal expansion mismatch between adhesive and substrate can lead to bond failure.
- Oxidation and chemical degradation can weaken adhesive bonds over time.
Innovations in High-Temperature Adhesives
- Advanced formulations incorporate heat-resistant additives to enhance adhesive performance.
- Ceramic-filled adhesives offer exceptional stability and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures.
- Silicone-based bonds are known for their thermal stability and flexibility.
Key Considerations in Selecting High-Temperature Adhesives
- Temperature range:Choose adhesives with suitable operating temperature limits.
- Substrate compatibility:Ensure the adhesive adheres well to the specific metal surfaces.
- Thermal conductivity: High thermal conductivity can help mitigate thermal stress.
Design and Application Challenges
- Joint design must account for differential expansion and contraction under heat.
- Stress distribution across the bonded area is crucial to prevent localized weakening.
- Precise application and curing techniques are necessary for optimal performance.
Benefits of High-Temperature Resistant Bonds
- Enhanced reliability:Adhesive bonds that endure high temperatures maintain structural integrity.
- Weight reduction: High-temperature adhesives can replace traditional bulky fasteners.
- Improved performance: Industries like aerospace benefit from lighter components without sacrificing strength.
Real-World Applications
- Aerospace:Adhesive bonds in engine components and aircraft structures must withstand extreme heat and thermal cycling.
- Automotive: High-temperature adhesives find use in exhaust systems, engines, and brake assemblies.
- Electronics: Bonding in electronic devices where heat dissipation is crucial requires specialized adhesives.
Testing and Quality Assurance
- Rigorous testing under simulated high-temperature conditions is essential.
- Non-destructive evaluation methods verify bond integrity and longevity.
Ensuring Long-Term Durability
Achieving long-term durability in metal bonding adhesives is crucial to their performance, especially in industries where reliability is paramount. To ensure a long-lasting adhesive bond, one must consider several key factors:
- Material Selection:Choosing a suitable adhesive material is fundamental. High-quality adhesives with proven track records in bonding metals provide a strong foundation for durability. People often favor epoxy, polyurethane, and cyanoacrylate adhesives for their robustness.
- Compatibility with Substrates:Adhesives must be compatible with the specific metal substrates they are bonding. Considering the metallurgical composition, surface roughness, and potential galvanic corrosion effects is essential. Adequate surface preparation guarantees optimum adhesion.
- Adhesive Application and Cure:Adhesives should be applied following manufacturer guidelines, ensuring uniform coverage and proper thickness. Adequate curing time and conditions, such as temperature and humidity, are critical to achieving optimal bond strength and durability.
- Mechanical Properties:Adhesives must exhibit mechanical properties that match or exceed the application’s demands. Factors like shear strength, tensile strength, and flexibility play a role in the adhesive’s ability to withstand stress and load over time.
- Environmental Resistance:Long-term durability hinges on the adhesive’s ability to resist environmental factors. These exposures encompass moisture, chemicals, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation. Adhesives with enhanced resistance to these conditions maintain bond integrity.
- Fatigue and Creep Resistance: In applications subject to repeated loading or sustained stress, fatigue and creep resistance are critical. Adhesives that withstand these effects ensure the bond remains intact, even under prolonged use.
- Quality Control and Testing:Rigorous quality control during adhesive production and bond creation is indispensable. Regular testing, including mechanical, thermal, and environmental tests, helps identify potential weaknesses and ensures consistent performance.
By meticulously addressing these factors, manufacturers and engineers can ensure the long-term durability of metal bonding adhesives. This enhancement not only boosts the reliability of the final product but also reduces maintenance costs and improves overall safety in various industries.
Compatibility with Different Metal Alloys
Metal bonding adhesives are critical in achieving durable and reliable bonds between various metal alloys. Ensuring compatibility across a broad spectrum of metal compositions is essential for applications ranging from manufacturing to construction. Key factors that contribute to the compatibility of these adhesives with different metal alloys include:
- Chemical Formulation:The adhesive’s chemical composition plays a pivotal role in its ability to form strong bonds with various metals. Adhesive formulations are often optimized to establish chemical interactions with specific metal surfaces, enhancing adhesion strength and long-term stability.
- Surface Preparation:Proper surface preparation is imperative to optimize bonding between the adhesive and metal alloys. One should clean, degrease, and, if needed, treat surfaces with primers to enhance adhesion. Different metals require specific surface treatments to promote chemical compatibility.
- Thermal Expansion Matching: Mismatched thermal expansion coefficients between metals can lead to stress and bond failure over time. Adhesives designed with similar thermal expansion properties to those of the bonded metal alloys can mitigate these issues, ensuring stability under temperature variations.
- Electrochemical Compatibility:Electrochemical interactions also influence the compatibility of different metal alloys in bonding adhesives. Galvanic corrosion can occur when dissimilar metals are in contact, leading to bond degradation. Manufacturers can formulate adhesives to act as barriers against such decline.
- Load-Bearing Characteristics:The load-bearing capacity of the adhesive-metal bond is crucial, especially in structural applications. Adhesives must exhibit consistent performance across diverse metal alloys, maintaining strength under various loading conditions.
- Environmental Resistance:Compatibility extends to ecological factors such as moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure. Adhesives need to withstand these conditions while maintaining bond integrity over time. Formulating adhesives that can resist specific environmental challenges is essential for long-term durability.
The compatibility of metal bonding adhesives with different metal alloys involves a comprehensive approach encompassing chemical formulation, surface preparation, thermal and electrochemical considerations, load-bearing capabilities, and environmental resistance. By addressing these aspects, manufacturers can ensure reliable bonds that meet the demands of various industries and applications.
Quality Control and Testing Standards
Ensuring the reliability and safety of metal bonding adhesive applications requires stringent quality control and adherence to established testing standards. The following bullet points highlight the key aspects of quality control and testing in metal bonding adhesive applications:
1.Adhesive Compatibility: Thorough assessment of adhesive compatibility with specific metal substrates is crucial to prevent adhesion failure or corrosion.
2.Material Preparation:Proper surface preparation is essential for optimal adhesion and bonding strength. This task involves cleaning, degreasing, and potentially applying primers.
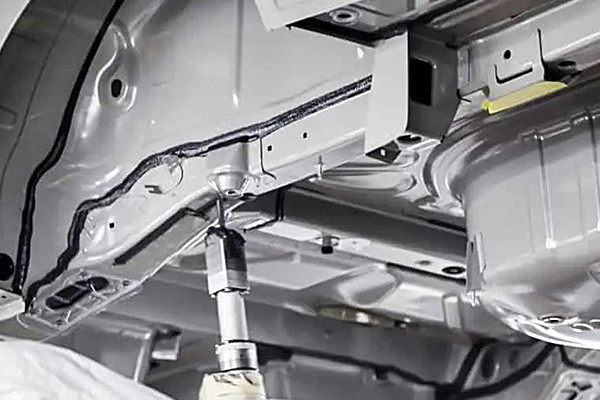

3.Bond Strength Testing:Various methods such as lap shear, tensile, and peel tests are employed to evaluate the strength of adhesive bonds, providing insight into their structural integrity.
4.Environmental Testing:Adhesives are subjected to environmental stressors like temperature variations, humidity, and chemical exposure to determine their performance under real-world conditions.
5.Accelerated Aging Tests:Simulating long-term aging through accelerated tests helps predict the adhesive’s durability and resistance to degradation over time.
6.Shear Fatigue Testing:Particularly relevant for dynamic loads, shear fatigue tests replicate cyclic stresses to assess the adhesive’s ability to withstand repeated strain.
7.Adhesive Thickness Control:Ensuring consistent adhesive thickness across the joint area is essential for uniform stress distribution and reliable bonding.
8.Non-Destructive Testing:Techniques like ultrasonic, X-ray, and thermal imaging detect defects or voids in adhesive joints without compromising the structure’s integrity.
9.Quality Control Protocols:Implementing robust quality control protocols at every stage, from material selection to application and curing, minimizes the risk of defects and ensures consistent results.
10.Standard Compliance:Adherence to industry-specific standards like ASTM or ISO helps validate adhesive performance and guarantees that the end product meets regulatory requirements.
11.Real-time Monitoring:Sensor technologies during bonding and curing processes allow real-time monitoring of critical parameters, enhancing process control and bond quality.
12.Data Analysis:Collecting and analyzing data from testing and monitoring processes enables continuous improvement, leading to optimized adhesive formulations and application techniques.
By rigorously following these quality control practices and testing standards, manufacturers can ensure the reliability, safety, and longevity of metal bonding adhesive applications across diverse industries.
Innovations in Metal Bonding Adhesive Technology
Metal bonding adhesive technology is undergoing dynamic transformations fueled by breakthroughs and market demands. Notable innovations shaping the future of metal bonding adhesives include:
- Nanoengineered Adhesives:Integrating nanomaterials into adhesive formulations enhances bonding strength, corrosion resistance, and overall durability of metal joints, catering to high-performance applications.
- Hybrid Bonding Solutions:Emerging hybrid adhesives, combining the advantages of traditional structural adhesives with mechanical fasteners, offer a versatile approach to meet diverse requirements in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
- Cold Welding Adhesives:Adhesives capable of inducing cold welding at the metal interface provide an alternative to traditional welding methods, enabling solid and efficient bonds without high temperatures.
- Innovative Monitoring Adhesives:Incorporating sensors and monitoring capabilities into adhesive systems allows real-time assessment of bond quality, enabling predictive maintenance and ensuring structural integrity.
- Environmentally Friendly Adhesives:Increasing environmental concerns drive the development of metal bonding adhesives free from hazardous substances and offer low VOC emissions, aligning with sustainability goals.
- High-Temperature Resistant Adhesives:Industries like aerospace and energy require adhesives capable of withstanding extreme temperatures; innovations in this area ensure reliable bonding in challenging environments.
- Digital Twin Integration:Coupling adhesive bonding processes with digital twin simulations enhances process optimization and quality control, reducing errors and improving overall efficiency.
- Customizable Bonding Solutions:Adhesive formulations can be customized to specific metal substrates and application needs for optimized performance, resulting in cost-effective and reliable bonding solutions.
As these innovations unfold, the landscape of metal bonding adhesive technology is poised to revolutionize industries by providing enhanced performance, improved efficiency, and greater flexibility in joining metal components.
Nano-adhesives: Pushing the Boundaries
In metal bonding adhesives, a revolutionary breakthrough has emerged – nano-adhesives. These remarkable materials, engineered at the nanoscale, offer unprecedented bonding strength, durability, and versatility possibilities. As industries strive for ever-improving performance, nano-adhesives push the boundaries of what was once thought possible.
Nanoscale Engineering for Superior Performance
- Nano-adhesives are formulated using nanoparticles, often with diameters less than 100 nanometers.
- At this scale, researchers can harness the unique properties of materials to enhance adhesive performance.
Unmatched Bonding Strength
- Nano-adhesives create adhesive bonds at the molecular level, resulting in solid connections.
- The increased surface area of nanoparticles allows for more contact points between the adhesive and the substrate.
Enhanced Durability and Resistance
- Nano-adhesives can resist wear, environmental factors, and even corrosion more effectively.
- The inherent properties of nanoparticles contribute to improved resistance to heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress.
Tailored Properties for Diverse Applications
- The flexibility of nano-adhesive formulations enables customization for specific applications.
- Electrical conductivity, thermal insulation, and optical transparency can all be optimized.
Challenges and Innovations
- Precise manufacturing and dispersion of nanoparticles are critical for consistent adhesive performance.
- Researchers are exploring novel nanoparticles and binders to address various challenges.
Aerospace and Beyond: Real-World Applications
- The aerospace industry benefits from nano-adhesives in aircraft assembly, as these high-strength bonds can withstand extreme conditions.
- The Electronics sector utilizes nano-adhesives for miniature device assembly, ensuring reliable connections.
Sustainability and Efficiency
- Nano-adhesives often require minimal application, reducing material waste.
- Their exceptional strength allows for lightweight designs, enhancing energy efficiency.
Future Prospects
- Ongoing research aims to refine nano-adhesive formulations for even broader applications.
- Nanotechnology continues to evolve, opening doors to new possibilities in bonding technology.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
- As with any advanced material, responsible use and disposal of nano-adhesives are crucial.
- Stakeholders are developing regulations and guidelines to ensure safe implementation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Metal bonding adhesives have undergone a transformative shift in recent years, not only in terms of their performance but also in their environmental impact. As industries strive to adopt more sustainable practices, focusing on eco-friendly adhesive solutions has become paramount. This section delves into the environmental and sustainability aspects of metal bonding adhesives, highlighting key trends and strategies.
Reduced VOC Emissions and Hazardous Chemicals
- Manufacturers are actively working to minimize the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in metal bonding adhesive formulations.
- There is a concerted effort to eliminate or reduce hazardous chemicals in adhesive compositions, contributing to safer workplace environments and reducing harm to ecosystems.
Bio-based and Biodegradable Formulations
- The emergence of bio-based adhesives derived from renewable resources represents a significant step towards sustainability in metal bonding.
- Biodegradable adhesive options are gaining traction, ensuring that sticky residues break down naturally and not contribute to long-term environmental pollution.
Life Cycle Assessment and Eco-Labeling
- Adopting life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies allows adhesive manufacturers to evaluate the environmental impact of their products across their entire life cycle.
- Eco-labeling initiatives, such as certifications from reputable organizations, provide consumers with transparent information about the environmental attributes of metal bonding adhesives.
Energy-Efficient Application Processes
- The trend towards energy efficiency extends to the application processes of metal bonding adhesives, focusing on reducing energy consumption during curing and bonding.
- Low-temperature curing adhesives save energy and enable the bonding of temperature-sensitive substrates.
Waste Reduction and Circular Economy
- Adhesive manufacturers are exploring strategies to minimize waste during production and application, aligning with the principles of a circular economy.
- Efforts to facilitate adhesive removal and substrate separation at the end of product life promote the recycling and reuse of materials, reducing the overall environmental footprint.
Collaboration and Industry Partnerships
- Industries and adhesive manufacturers collaborate to develop sustainable solutions tailored to specific applications and sectors.
- Joint research projects and partnerships ensure that adhesive formulations meet industry standards while addressing environmental concerns.
Future Prospects and Emerging Trends
In recent years, adhesive technology has witnessed significant advancements, particularly in metal bonding. As industries continue to demand more robust and more durable bonding solutions for various applications, metal bonding adhesives are garnering increasing attention. This section explores the prospects and emerging trends in this dynamic area of adhesive development.
Advancements in Formulations and Performance
The future of metal bonding adhesives lies in continuously improving their formulations and performance characteristics. Manufacturers invest in research and development to create bonds that offer superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and chemical stability. The emergence of nanotechnology allows for the incorporation of nanoparticles into adhesive formulations, enhancing their mechanical properties and durability. Furthermore, the development of adhesives with tailored properties for specific metals and alloys is on the rise, enabling a more comprehensive range of applications across industries.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
With the growing emphasis on sustainability, the adhesive industry is shifting towards more environmentally friendly formulations. Future trends in metal bonding adhesives include reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous chemicals in adhesive compositions. Manufacturers are also exploring bio-based and biodegradable adhesive options, aligning with the global push for greener solutions. This eco-conscious approach addresses environmental concerns and meets evolving regulatory standards.
Integration of Smart Technologies
Integrating intelligent technologies within metal bonding adhesives is an intriguing prospect. Researchers are investigating incorporating sensors, nanoparticles, and self-healing mechanisms into adhesive matrices. These innovations would allow adhesives to monitor structural integrity, provide real-time stress distribution data, and even damage minor damages autonomously. Such advancements promise for industries where safety and reliability are paramount, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Industry-specific Customization
As various industries have unique bonding requirements, the future of metal bonding adhesives will likely involve greater customization. We anticipate that adhesive manufacturers will forge closer collaborations with electronics, construction, and energy initiatives to create customized solutions. This trend aligns with the increasing demand for adhesives that cater to specific metal types, environmental conditions, and application methods.
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial advancement, metal bonding adhesives have established themselves as indispensable tools for achieving robust, reliable, and innovative solutions. Their ability to create seamless bonds between various metal substrates, while overcoming challenges such as temperature variations and compatibility issues, has paved the way for their widespread adoption across sectors like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction. As technology continues to progress, further refinements and breakthroughs are anticipated, cementing metal bonding adhesives’ position as a cornerstone of modern engineering and manufacturing.