Pressure Sensitive Adhesive
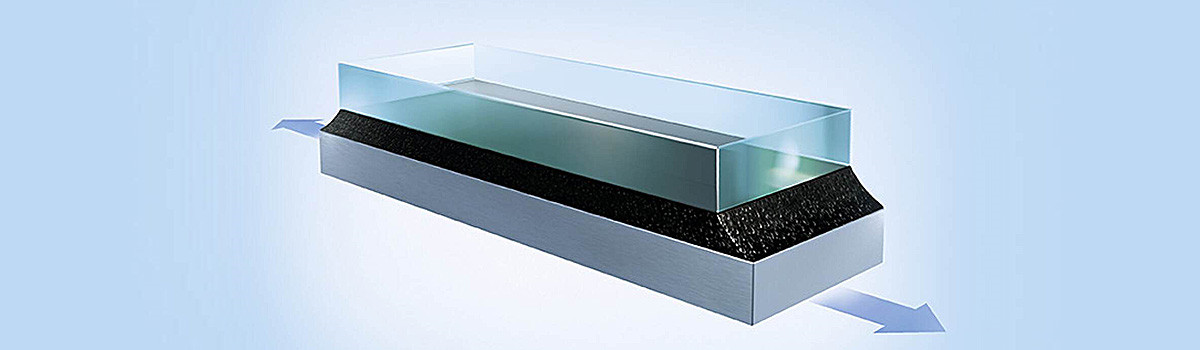
In today’s fast-paced world, the subtle yet indispensable role of pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) often goes unnoticed, despite its widespread presence in our daily lives. From the notes that stick on our refrigerator doors to the labels on our packaged goods, PSA is a versatile marvel that simplifies tasks with remarkable ease. Its ingenious design enables objects to bond securely without needing heat or solvent activation, making it an effortless solution for various applications.
One of the most palpable aspects of PSA is its user-friendly nature. It offers a convenient and instant bonding solution that requires no additional tools or complex procedures. Whether hanging decorations during festive seasons or mending torn paper, the simplicity of PSA ensures that anyone, regardless of their skill level, can achieve effective results. Furthermore, the residue-free removal characteristic of many PSA products underscores its adaptability, allowing for repositioning or replacement without leaving behind unsightly marks or damaging surfaces.
PSA’s impact extends far beyond our domestic spheres. Industries ranging from packaging and electronics to automotive and medical devices rely heavily on this adhesive technology. It’s easy application and reliability make it ideal for manufacturers seeking efficient and consistent assembly processes. Whether securing critical components in a medical device or ensuring automotive parts stay firmly in place, PSA’s role in enhancing precision and ease cannot be overstated.
What is Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA), and how does it work?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) is an adhesive that forms a bond when applying pressure. It is commonly used in various applications such as tapes, labels, stickers, and other bonding materials. Unlike other adhesives that require heat, water, or chemical reactions to activate their bonding properties, PSAs bond to surfaces simply by applying pressure.
The critical characteristics of PSA include:
- Stickiness: PSAs are designed to be tacky or sticky at room temperature. This stickiness allows them to adhere to surfaces without additional factors like heat or solvents.
- No Additional Substances Needed: Unlike traditional adhesives that might require curing time, moisture, or heat to create a strong bond, PSAs work on their own with just the application of pressure.
- Removability: Many PSAs offer the advantage of being removable without leaving a significant residue behind or damaging the surface to which they were applied. This makes them popular for temporary applications like stickers or masking tape.
- Variability: PSAs come in a range of formulations, allowing for different levels of tackiness, strength, and flexibility to suit various applications.
The mechanism behind how PSAs work involves the adhesive material’s molecular properties and the interaction between the adhesive and the surface it’s being applied to:
- Wet Tack: When pressure is applied to the PSA, the adhesive conforms to the microscopic irregularities on the surface. This creates a larger contact area between the cement and the character, increasing the attractive forces (van der Waals forces) between them. This initial stickiness is often referred to as “wet tack.”
- Flow and Creep: Over time, the adhesive continues to flow and spread under pressure, further enhancing the contact area and strengthening the bond. This phenomenon is known as “creep.”
- Cold Flow: Even after the initial application, PSAs can continue to flow and adapt to surface irregularities, helping them maintain their bond.
- Van der Waals Forces: The bond strength in PSAs is mainly due to van der Waals forces, which are weak attractive forces between molecules. These forces play a significant role in the adhesion of PSAs to surfaces.
It’s important to note that temperature can affect the performance of PSAs. Extremely low temperatures can make the adhesive material stiff and less tacky, while high temperatures can make it softer and more prone to flow excessively.
Which industries extensively use Pressure Sensitive Adhesives for their products?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) are versatile adhesive materials that form a bond when pressure is applied without needing heat or solvent activation. They are widely used across various industries due to their ease of use, flexibility, and ability to create temporary or permanent bonds on multiple substrates. Some industries that extensively use Pressure Sensitive Adhesives for their products include:
- Packaging Industry: PSAs are commonly used for sealing boxes, attaching labels, and securing various types of packaging materials together.
- Automotive Industry: PSAs are used for attaching trim components, bonding interior panels, mounting exterior emblems, and even assembling electronic components within vehicles.
- Medical Industry: Medical tapes, bandages, wound dressings, and various medical devices often utilize PSAs due to their gentle yet secure adhesive properties.
- Consumer Electronics: PSAs are used for bonding components in electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable technology.
- Construction and Building: PSAs are used in applications like mounting mirrors, attaching signage, securing flooring materials, and bonding insulation.
- Labeling and Graphics: Labels, decals, stickers, and graphics in retail, food and beverage, and industrial products use PSAs extensively.
- Aerospace and Aviation: PSAs are used for attaching lightweight materials, insulation, and sealing components in the aerospace industry.
- Furniture and Furnishings: PSAs can be found in furniture assembly, including attaching foam padding, upholstery, and decorative elements.
- Textile Industry: PSAs are used in fabric bonding, hemming, and temporary fabric attachments.
- Healthcare and Hygiene: PSAs are used in diapers, feminine hygiene products, and wound care items for their secure yet gentle adhesive properties.
- Stationery and Office Supplies: Items like sticky notes, tape, and other adhesive office supplies often use PSAs.
- Renewable Energy: PSAs assemble solar panels, wind turbine components, and battery systems.
- Footwear Industry: PSAs are used in shoe manufacturing for attaching soles, insoles, and decorative elements.
- Transportation Industry: PSAs are used for various bonding applications in the railway, marine, and transportation sectors.
- Sporting Goods: Equipment like rackets, bats, and protective gear use PSAs for bonding various components.
These are just a few examples of industries that rely extensively on Pressure Sensitive Adhesives for their products. The versatility and ease of use of PSAs make them a preferred choice for various applications across a wide range of sectors.
How does Pressure Sensitive Adhesive simplify routine tasks compared to traditional adhesives?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) are a type of adhesive that forms a bond when pressure is applied to join two surfaces. They are known for their ability to stick to a wide variety of surfaces with just light pressure, without the need for heat, water, or solvent activation. This unique characteristic offers several advantages that can simplify routine tasks compared to traditional adhesives:
- Ease of Application:PSAs are easy to apply since they don’t require any specialized equipment or additional processes. You simply apply pressure to the adhesive-coated surface, and it sticks. This simplifies the application process, reducing the need for complex setups or tools.
- No Curing Time:Unlike some traditional adhesives that require a curing or drying time, PSAs bond immediately upon application of pressure. This can significantly reduce the waiting time needed before moving on to the next steps of a task.
- Less Mess and Cleanup:Traditional adhesives often involve mixing and application processes that can be messy and require careful cleanup to avoid residue. PSAs, on the other hand, are typically applied as a pre-coated film or tape, minimizing the chances of spills, drips, or excess adhesive that need to be cleaned up.
- Versatility:PSAs can adhere to a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, glass, paper, fabrics, and more. This versatility means that you don’t need to use different adhesives for different materials, simplifying the selection and inventory management processes.
- No Heat or Solvents:Some traditional adhesives require heat or the use of solvents to activate or set. This can complicate processes, require specialized equipment, and introduce safety considerations. PSAs eliminate the need for heat or solvents, making the tasks safer and more straightforward.
- Immediate Bond Strength:PSAs often provide immediate bond strength upon application of pressure. Traditional adhesives might need time to cure or set before achieving full strength. This faster bond strength can streamline production processes and improve overall efficiency.
- On-the-Spot Repairs:Due to their easy application and immediate bonding properties, PSAs are excellent for quick repairs and fixes. They allow for on-the-spot solutions without the need for extended downtime or waiting periods.
- Reduced Production Costs:The simplicity of application and reduced need for specialized equipment, heat, or solvents can lead to cost savings in terms of labor, energy, and equipment maintenance.
- Consistency:The uniform application of PSA films or tapes ensures a consistent bond across surfaces, reducing the likelihood of inconsistencies that might occur with manually applied traditional adhesives.
- Removability and Reusability:Many PSAs are designed to be removable without leaving residue or damaging surfaces. This can be advantageous for temporary applications or when repositioning is needed.
While PSAs offer these advantages, it’s important to note that they might not be suitable for all applications. Some tasks may require the specific properties of traditional adhesives, such as high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, or structural strength. The choice between PSAs and traditional adhesives depends on the specific requirements of the task at hand.
What are the primary components that make Pressure Sensitive Adhesive unique?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) adhere to surfaces when light pressure is applied without needing heat, water, or solvent activation. Several primary components make Pressure Sensitive Adhesives unique:
- Polymeric Matrix: The base of a PSA is a polymeric matrix, which provides the adhesive’s cohesive strength and flexibility. This matrix is typically made from acrylics, silicones, rubber-based compounds, or other polymers.
- Tackifier: A tackifier is an additive that enhances the initial tack or stickiness of the adhesive. It helps the adhesive bond quickly to surfaces upon contact. Tackifiers are often resins or low molecular-weight polymers that improve the adhesive’s ability to form a bond under light pressure.
- Modifiers: Various modifiers can be added to PSAs to adjust their properties. These may include plasticizers (to increase flexibility), stabilizers (to improve shelf life and resistance to environmental factors), and fillers (to modify properties like viscosity and adhesion).
- Solvents and Water: Unlike other adhesives that require heat or solvents for activation, PSAs remain permanently tacky at room temperature. They don’t need any additional substances to facilitate bonding, which sets them apart from other adhesive types.
- Release Liner: PSAs often come with a release liner, a protective backing removed before applying the adhesive. The liner prevents the adhesive from sticking to unintended surfaces and maintains its tackiness until ready for use.
- Viscoelastic Behavior: One of the critical characteristics of PSAs is their viscoelastic behavior. This means they combine the properties of both liquids (viscous) and solids (elastic). They flow like liquids under pressure but return to their original shape once the pressure is released. This property enables them to conform to uneven surfaces and maintain a strong bond even when applying slight pressure.
- Instant Adhesion: PSAs exhibit instant or near-instant adhesion upon contact with a surface. This is because the molecular forces between the adhesive and the substrate are relatively weak, allowing them to form bonds without extensive pressure or curing time.
- Removability: Another unique aspect of PSAs is that they can often be removed from surfaces without leaving significant residue or damaging the substrate. This is due to their relatively weak bond strength compared to other adhesives.
- Wide Range of Applications: PSAs are versatile and find use in various industries and applications, including packaging, labeling, medical devices, automotive assemblies, electronics, and more. Their ability to bond to different surfaces, including metals, plastics, glass, and paper, adds to their versatility.
Overall, the combination of tackiness, instant adhesion, viscoelastic behavior, and versatility makes Pressure Sensitive Adhesives unique and widely applicable in many everyday and industrial situations.
Which materials are compatible with Pressure Sensitive Adhesive bonding?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) bonding is an adhesive bonding where the adhesive remains tacky and adheres to surfaces under light pressure without heat or solvent activation. This type of adhesive is commonly used in applications like labels, tapes, decals, and other temporary or semi-permanent attachments. PSA bonding is compatible with a wide range of materials, including:
- Paper and Cardboard: PSA adhesives can bond effectively to paper and cardboard surfaces, making them ideal for labels, tapes, and other paper-based applications.
- Plastic Films: Many plastic films, including polyethylene, polypropylene, polyester (Mylar), and PVC, can be bonded using PSAs. These applications are expected in packaging, graphics, and labeling.
- Metal: Smooth metal surfaces, such as aluminum, steel, and coated metals, can be effectively bonded with PSAs. They are often used in mounting signs, nameplates, and decorative elements.
- Glass: While glass is generally non-porous, some PSAs are formulated to adhere to glass surfaces. These are used in applications like window graphics and glass decorations.
- Wood: PSAs can adhere to various types of wood surfaces, including finished wood, plywood, and particleboard, making them suitable for applications like woodworking and carpentry.
- Foam: Foam materials, like polyurethane foam and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, can be bonded using PSAs. This is common in applications where cushioning or padding is required.
- Textiles: Certain PSAs are designed to adhere to fabrics and materials, making them useful for applications like clothing labels and temporary fabric attachments.
- Rubber and Elastomers: Some rubber and elastomeric materials can be bonded using PSAs. This is common in gasketing and sealing applications.
- Ceramics: In some cases, PSAs can bond to ceramics and ceramic-coated surfaces, although the success of the bond may vary based on the specific adhesive and ceramic composition.
- Low-Energy Surfaces: Some PSAs are designed to bond to low-energy surfaces, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, which are traditionally challenging to adhere to.
It’s important to note that not all PSAs are universally compatible with all materials. The choice of PSA should be based on factors like the specific materials being bonded, the application requirements (such as temperature resistance, outdoor exposure, or removability), and any potential interactions between the adhesive and the substrate. Compatibility tests and consulting with adhesive manufacturers are recommended to ensure successful bonding for your specific application.
How does the bonding strength of PSA vary based on different surfaces?
The bonding strength of Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) can vary significantly based on the type of surface they are applied to. PSAs are unique because they adhere to surfaces using pressure without additional heat, water, or solvent activation. The bonding strength is influenced by several factors related to both the adhesive and the cover:
- Surface Energy: The surface energy of a material determines its receptiveness to adhesion. High surface energy materials, like metals and glass, provide better adhesion for PSAs because they allow for stronger molecular interactions between the adhesive and the surface.
- Substrate Roughness: A rough surface provides more area for the adhesive to contact, leading to stronger adhesion. Smooth surfaces might have reduced contact points and weaker bond strength.
- Porosity: Porous surfaces, such as paper or certain types of wood, can absorb the adhesive, leading to a stronger bond. Non-porous surfaces might not allow the adhesive to penetrate, resulting in a weaker bond.
- Cleanliness: The cleanliness of the surface is crucial for solid adhesion. Contaminants, oils, dust, and other particles can interfere with the adhesive’s ability to bond correctly.
- Surface Treatments: Some surfaces might undergo corona, plasma, or chemical priming to increase their surface energy and improve adhesive bonding.
- Temperature: Temperature can affect the viscosity of the adhesive and the ability to form a strong bond. Some PSAs are sensitive to temperature changes and may perform differently at different temperatures.
- Dwell Time: The amount of time pressure applied affects the adhesive’s ability to create molecular solid interactions with the surface.
- Peel Angle and Speed: The angle at which you peel the adhesive and the speed at which you peel it can impact the bond strength. Sometimes, the bond might be more robust when peeled at a certain angle or speed.
- Chemical Compatibility: Some PSAs might be chemically incompatible with certain surfaces, leading to weaker bonds or adhesive failure.
- Adhesive Formulation: The composition of the PSA itself can play a role. Different types of PSAs (acrylic, rubber-based, silicone-based, etc.) have varying levels of adhesion to other surfaces.
Due to these complex interactions, the bonding strength of PSAs can vary widely depending on the specific adhesive, the substrate material, and the conditions under which the adhesive is applied. Manufacturers often provide guidelines and recommendations for optimal bonding based on the types of surfaces involved. It’s important to conduct testing and consider these factors when selecting a PSA for a particular application.
What are some everyday household items that utilize Pressure Sensitive Adhesives?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) are widely used in everyday household items due to their convenience and ease of application. These adhesives are tacky at room temperature and adhere firmly when pressure is applied. Here are some examples of household items that utilize PSAs:
1.Post-it Notes: These sticky notes use PSAs to allow users to attach them to surfaces temporarily and easily remove them without leaving residue.

2.Tape: Various types of video, such as masking tape, duct tape, and electrical tape, utilize PSAs for their adhesive properties.
3.Sticky Tapes: Transparent tape, Scotch tape, and other clear tapes used for wrapping gifts, attaching lightweight items, and general household tasks often rely on PSAs.
4.Bandages: Many adhesive bandages (band-aids) use PSAs to stick to the skin securely without causing discomfort during removal.
5.Decals and Stickers: Decorative decals, wall stickers, laptop stickers, and bumper stickers are commonly made with PSAs.
6.Hooks and Hangers: Removable adhesive hooks and hangers stuck to walls, doors, or other surfaces are often equipped with PSAs.
7.Contact Paper: Self-adhesive contact paper for covering shelves, lining drawers, or redecorating surfaces typically relies on PSAs.
8.Plastic Wrap and Cling Film: Some plastic wraps and cling films use PSAs to stick to containers or food items for sealing and preserving.
9.Lint Rollers: Lint rollers, used to remove lint and pet hair from clothing and furniture, employ PSAs to make the sticky sheets adhere effectively.
10.Carpet Tape: Double-sided carpet tape uses PSAs to secure carpets and rugs in place without needing permanent adhesion.
11.Medical Tapes: Certain medical tapes, like first aid and surgical videos, use PSAs to adhere to the skin without causing harm.
12.Labels: Self-adhesive labels used for labeling items, addressing envelopes, and organizing often utilize PSAs.
13Packaging Tapes: Packaging tapes with adhesive backing used for sealing boxes and packages typically rely on PSAs.
14.Mounting Squares and Strips: These are used to mount lightweight items on walls without nails or screws and are often equipped with PSAs.
15.Mouse Pads: Some mouse pads feature a sticky bottom surface that adheres to the desk or table using PSAs.
16.Screen Protectors: Many screen protectors for devices like smartphones and tablets use PSAs to stick to the screen’s surface.
17.Non-slip Pads: Non-slip pads for furniture, such as table and chair legs, use PSAs to prevent slipping.
These are just a few examples of everyday household items that utilize Pressure Sensitive Adhesives. The versatility and convenience of PSAs make them a valuable component in various products that enhance our daily lives.
How has Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) transformed the world of arts and crafts?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) has significantly impacted the world of arts and crafts by providing a versatile and user-friendly method of adhering materials together. Here’s how PSA has transformed this creative domain:
- Ease of Use: PSA is effortless, often in the form of tapes or sticky-backed sheets. Unlike traditional glues or adhesives that may require mixing, drying time, or special application techniques, PSA can be applied simply by pressing the adhesive surface onto the desired material. This ease of use makes it accessible to people of all ages and skill levels, making arts and crafts projects more achievable and enjoyable.
- Precision: PSA allows for precise application. Crafters can position materials precisely where they want them before applying pressure to secure them. This precision is precious for intricate projects that involve delicate elements.
- No Mess: Unlike liquid glues or adhesives that can be messy and require careful handling, PSA eliminates the risk of spills, drips, or excess adhesive. This makes crafting cleaner and more convenient, especially when working with children or in confined spaces.
- Versatility: PSA comes in a wide range of formulations and materials, from double-sided tapes to foam tapes to removable adhesives. This versatility allows crafters to choose the suitable adhesive for their specific project needs, whether working with paper, fabric, wood, plastics, or other materials.
- Quick Bonding: PSA typically provides instant or rapid bonding upon application of pressure. This means crafters can move forward with their projects without waiting for drying times, reducing frustration and allowing for a smoother creative process.
- Repositioning: Many PSAs offer temporary bonding that allows for the repositioning of materials before a more permanent bond is formed. This is especially valuable when experimenting with layouts or working on projects requiring careful alignment.
- Clean Finish: PSA often creates a clean, neat finish without visible adhesive lines or residue, which is essential for maintaining artistic creations’ aesthetic quality.
- Adhesion Variety: Depending on the adhesive chosen, PSA can provide a range of adhesion strengths, from temporary bonds that can be easily removed without damaging surfaces to strong permanent bonds that hold up over time.
- Reduced Dry Time: Unlike traditional liquid adhesives that require drying time, PSA bonds immediately upon application of pressure. This accelerates the creative process and allows for more efficient project completion.
- Innovative Techniques: PSA has inspired new crafting techniques and projects that leverage its unique properties. For instance, artists and crafters may use PSA to create interactive elements, such as pop-up cards, or to incorporate layers of materials easily.
In essence, Pressure Sensitive Adhesive has revolutionized the arts and crafts world by simplifying the process of adhering materials together, enhancing precision, reducing mess, and enabling a broader range of creative possibilities. It has become an essential tool in the toolkit of artists and crafters, allowing them to bring their ideas to life more efficiently and with greater precision.
What are the environmental advantages of using Pressure Sensitive Adhesives?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) offer several environmental advantages compared to other types of adhesives. These advantages stem from their unique properties and application methods. Here are some of the ecological benefits of using PSAs:
- Reduced VOC Emissions:Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are chemicals that can contribute to air pollution and adversely affect human health and the environment. PSAs are typically solvent-free or have shallow VOC content, as they do not require solvents or water for application. This reduces the emission of harmful chemicals into the atmosphere.
- Energy Efficiency:PSAs do not require heat or water for application, unlike other adhesives that may require energy-intensive processes like drying or curing in ovens. The absence of such techniques reduces energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
- Minimal Waste Generation:PSAs are typically supplied in rolls or sheets with release liners. The liners are often silicone-coated paper or film that prevents the adhesive from sticking to itself before application. These liners can be recycled, reducing waste generation. Additionally, the precision of PSA application minimizes excess adhesive use, leading to less waste.
- Ease of Application and Reduced Chemicals:PSAs adhere instantly upon application with light pressure, eliminating the need for additional chemicals, activators, or curing agents. This simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces the potential use of environmentally harmful substances.
- Low Energy Consumption During Bonding:PSAs require minimal pressure, often just finger or hand pressure, for adequate bonding. This contrasts with other adhesive types requiring high-pressure, high-temperature processes, resulting in lower energy consumption and less machinery wear and tear.
- Versatility and Reduced Packaging:PSAs can bond to various substrates, including plastics, metals, paper, and glass. Their versatility can reduce the need for different adhesive products and associated packaging, resulting in fewer materials used and less waste generated.
- Ease of Removal and Recycling:Many PSAs offer clean removability without leaving significant residues. This can be advantageous for recycling processes, reducing the need for extensive cleaning or chemical treatments before recycling.
- Long-Term Durability:High-quality PSAs are often designed to withstand various environmental conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and moisture exposure. This can extend the lifespan of products and reduce the need for replacements, thereby reducing resource consumption.
- Lower Environmental Impact in Transportation:PSAs are often lightweight and compact due to their adhesive properties, which can result in reduced transportation costs and associated environmental impacts (e.g., fuel consumption and emissions) during shipping.
While PSAs offer these environmental advantages, it’s essential to consider the entire life cycle of a product when assessing its environmental impact. This includes raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, usage, and end-of-life disposal. However, in many cases, the properties and application methods of PSAs can contribute positively to a product’s overall environmental footprint.
How do manufacturers ensure the longevity and reliability of PSA bonds?
Manufacturers do not typically issue or manage PSA (Public Service Announcement) bonds. Government entities or public institutions usually issue PSA bonds to fund infrastructure development, education, healthcare, and other public services. Therefore, the concept of manufacturers ensuring the longevity and reliability of PSA bonds is not applicable.
However, suppose you’re referring to PSL (Priority Sector Lending) bonds, which financial institutions issue to meet their mandated lending requirements to specific sectors of the economy. In that case, the following information might be relevant.
To ensure the longevity and reliability of bonds, regardless of the type, including PSL bonds, several measures are typically taken:
- Credit Analysis and Due Diligence:Before issuing bonds, the issuer (in this case, financial institutions) conducts a thorough credit analysis and due diligence on the borrower. This involves assessing the borrower’s financial health, repayment capacity, and the purpose of the funds being raised.
- Rating Agencies:The bonds are usually rated by credit rating agencies. These agencies assess the issuer’s creditworthiness and assign a credit rating to the bonds. Higher credit ratings indicate lower risk and higher reliability.
- Transparency and Disclosure:Issuers must provide accurate and comprehensive information about their financials, operations, and the purpose of the bonds. This transparency helps build investor trust and confidence.
- Legal Documentation:The terms and conditions of the bonds are laid out in legal documents such as the bond indenture or trust deed. These documents define the rights and obligations of both the issuer and the bondholders, helping ensure the bonds’ reliability.
- Monitoring and Reporting:Issuers often provide regular updates and reports to bondholders about their financial performance and the use of funds raised through the bonds. This transparency helps investors track the issuer’s progress and financial stability.
- Collateral or Security:In some cases, bonds might be backed by collateral or security assets. This provides an additional layer of protection for bondholders in case the issuer faces financial difficulties.
- Market Reputation:Established financial institutions with a strong market reputation are generally more likely to issue reliable bonds. A solid reputation is built over time through consistent financial performance and ethical business practices.
- Regulatory Oversight:Government agencies and regulatory bodies often oversee the issuance of bonds, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and investor protection measures.
- Risk Management:Issuers may implement risk management strategies to mitigate potential financial and operational risks that could affect the repayment of bonds.
- Investor Relations:Maintaining open lines of communication with investors and addressing their concerns or queries can build trust and ensure the bonds’ long-term reliability.
It’s important to note that the specific measures taken to ensure bond longevity and reliability can vary depending on the type of bond, issuer, and regulatory environment in which they operate.
What are the challenges faced when working with Pressure Sensitive Adhesive?
Working with Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) presents several challenges due to its unique characteristics and applications. Here are some of the main challenges faced when working with PSAs:
- Tack and Peel Performance: PSAs are designed to adhere instantly upon application of light pressure. Achieving the right balance of initial tack (adhesion) and peel strength (removability) can be challenging. It’s essential to ensure that the adhesive sticks well to the substrate while allowing for easy removal when needed.
- Substrate Compatibility: PSAs can vary in compatibility with different substrates. Some PSAs might adhere well to one surface type but could be better to another. Adhesion performance can be affected by factors such as surface energy, roughness, and substrate chemical composition.
- Temperature Sensitivity: PSAs can exhibit changes in adhesion properties with temperature variations. They might become too soft and lose adhesion at high temperatures or too rigid and lose flexibility at low temperatures. Selecting a PSA that performs well across a wide temperature range can be challenging.
- Aging and Environmental Factors: PSAs may degrade over time due to exposure to UV light, humidity, chemicals, and other environmental factors. This can lead to reduced adhesive performance and potentially compromised bond strength.
- Application Techniques: Applying PSAs evenly and avoiding air bubbles or wrinkles can be tricky, especially when dealing with large areas or intricate shapes. The application process requires precision and care to achieve optimal bond strength.
- Contaminants and Surface Preparation: Contaminants such as oils, dust, or residues on the substrate can interfere with adhesive performance. Proper surface preparation is crucial to ensure solid and lasting adhesion.
- Storage and Shelf Life: PSAs can have a limited shelf life, especially if not stored under appropriate conditions. Storage at high temperatures or exposure to moisture can lead to changes in adhesive properties over time.
- Peel Residue: When PSAs are removed, they might leave adhesive residue on the substrate. This can be undesirable for aesthetic reasons or when reapplication is necessary.
- Customization for Specific Applications: Different applications might require specific adhesive properties, such as resistance to chemicals, UV stability, flame resistance, or particular levels of adhesion. Finding or formulating a PSA that meets these specific requirements can be challenging.
- Regulatory Compliance: Depending on the application, PSAs might need to adhere to specific regulatory standards, especially in industries like healthcare or electronics. Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations can be complex.
- Removability: While many PSAs are designed for permanent bonding, some applications require the adhesive to be easily removable without damaging the substrate. Balancing adhesive strength with clean removability can be difficult.
To overcome these challenges, it’s essential to thoroughly understand the application requirements, choose the right type of PSA formulation, test adhesive properties on relevant substrates, and employ proper surface preparation and application techniques. Collaboration with adhesive manufacturers and experts can also help find solutions tailored to specific needs.
How does the ease of application of PSA contribute to its widespread usage?
The ease of application of Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) is one of the key factors contributing to its widespread usage in various industries and applications. This ease of application offers several benefits that make PSAs a preferred choice for bonding solutions:
1.No Need for Additional Equipment or Heat: PSAs do not require additional equipment such as solvents, heat, or curing processes to achieve bonding. They are applied simply by pressing the adhesive-coated surface onto the substrate, making the application process quick and straightforward.
2.Time Efficiency: The application of PSAs is usually a fast process, reducing the time required for bonding compared to other adhesive types that might need curing or drying times. This time efficiency can lead to increased productivity in manufacturing processes.
3.Reduced Labor and Training Costs: Since no specialized equipment or training is needed for applying PSAs, labor and training costs are generally lower. This makes PSA applications accessible to a broader range of personnel, leading to cost savings in training and operational expenses.
4.Consistency and Precision: PSA applications can be exact and consistent, especially when using automated or semi-automated application methods. This is important for industries that require uniformity in bonding across large volumes of products.
5.Less Mess and Waste: Unlike liquid adhesives that can spill, drip, or create waste due to excess application, PSAs are typically clean and result in minimal waste. This is particularly advantageous for applications where cleanliness and waste reduction are priorities.
6.Flexibility and Versatility: PSAs can be applied to various substrates, including irregular shapes and surfaces, without requiring complex adjustments. This versatility allows for creative and innovative design solutions in multiple industries.
7.Ease of Removal: Many PSAs are designed to be removable without leaving residue or damaging the substrate. This ease of removal is helpful in applications where temporary bonding or repositioning is required.
8.Adhesion to Different Surfaces: PSAs can adhere to various substrates, including plastics, metals, glass, and paper. Their ability to bond to diverse materials makes them suitable for multiple applications.
9.Reduced Downtime and Production Interruption: Since the PSA application is quick and doesn’t require curing or drying time, it helps reduce production downtime and interruption. This is especially important in industries with tight schedules.
10.Ease of Maintenance and Repair: PSAs can be quickly applied to restore or replace components without lengthy downtimes in applications where maintenance or repair is needed.
11.Accessibility: PSA products are widely available, and they come in various forms, such as tapes, sheets, and die-cuts. This accessibility makes it easy for businesses to source and integrate PSA solutions into their processes.
Overall, the ease of application of PSAs simplifies the bonding process, saves time and resources, and offers flexibility and convenience that contributes to their popularity and widespread usage in industries such as packaging, automotive, healthcare, electronics, construction, and more.
What role does Pressure Sensitive Adhesive play in the medical field?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) plays a crucial role in the medical field, particularly in the realm of wound care, medical devices, and wearable technology is a type of adhesive that forms a bond when pressure is applied to the need for heat and water, or solvents. This property makes it versatile and well-suited for various medical applications. Here are some ways in which PSA is used in the medical field:
- Wound Dressings and Bandages:PSA is to manufacture adhesive wound dressings and bandages. These products adhere gently to the skin, providing a barrier that protects wounds from contaminants while promoting healing. They are easy to apply, adjust, and remove without causing additional trauma to the wound area.
- Surgical Drapes and Tapes:During surgical procedures, PSA is used to secure surgical drapes and tapes that help create a sterile field. These adhesives are designed to stick securely to the patient’s skin and medical drapes, helping to maintain a clean and controlled environment in the operating room.
- Medical Tapes:PSA-based medical tapes are used to secure medical devices, such as catheters, tubes, and monitoring sensors, to the patient’s skin. They provide a secure and comfortable attachment, ensuring the appliances stay in place without causing skin irritation or discomfort.
- Transdermal Drug Delivery:Transdermal patches that deliver medications through the skin rely on PSA to adhere to the patient’s skin while gradually releasing the drug into the bloodstream. The adhesive helps maintain consistent contact with the skin, ensuring effective drug delivery over time.
- Ostomy Products:PSA is used to produce ostomy products, such as ostomy pouches and flanges. These products adhere to the skin around a stoma, providing a leak-proof seal and helping individuals with colostomies or ileostomies manage waste elimination.
- Wearable Medical Devices:Wearable medical devices, such as glucose monitors, ECG monitors, and fitness trackers, often use PSA to adhere to the skin. The adhesive ensures the appliances stay securely in place for accurate and continuous monitoring.
- Orthopedic Braces and Supports:PSA-based adhesives are used in orthopedic braces, tapes, and supports. These products help stabilize joints, support and manage pain in various musculoskeletal conditions.
- Diagnostics and Testing:PSA is used in various diagnostic applications, such as attaching electrodes for electrocardiograms (ECGs) and sensors for pulse oximetry. These applications rely on consistent skin contact for accurate measurements.
- Dental Applications:In dentistry, PSA is used to secure dental devices like braces, retainers, and dental prosthetics to the teeth or oral tissues.
The use of PSA in the medical field emphasizes its unique characteristics of easy application, comfortable wear, and secure attachment. However, it’s essential to ensure that PSA materials used in medical applications are safe, hypoallergenic, and biocompatible to avoid adverse patient reactions or complications.
When was Pressure Sensitive Adhesive first developed, and how has it evolved?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) was first developed in the early 20th century, with the initial patent for a pressure-sensitive adhesive tape being filed by R.D. Drew of Johnson & Johnson in 1928. However, the development of PSA can be traced back to earlier innovations in adhesive technology.
The early versions of PSA were based on natural rubber compounds, which exhibited the ability to adhere to surfaces under light pressure without needing heat or solvent activation. These early PSAs were used primarily in adhesive tapes and labels. The introduction of cellophane tape by 3M in the 1930s marked a significant milestone in the evolution of PSAs. This tape used a rubber-based PSA and was widely used during World War II for various applications.
Over time, the composition of PSAs has evolved significantly, leading to improved performance and versatility. Some key developments in the evolution of PSAs include:
- Synthetic Polymers: As artificial polymer technology advanced, rubber-based PSAs were gradually replaced with acrylic-based adhesives, which offered better stability, durability, and resistance to temperature and UV exposure.
- Hot Melt PSAs: In the 1960s, the development of hot melt PSAs introduced adhesives that could be applied in a molten state and solidified upon cooling. These adhesives were widely used in industries like packaging and labeling.
- Silicone-based PSAs: Silicone-based PSAs were introduced in the 1970s, offering excellent high-temperature resistance and low-temperature flexibility. They are used in applications where extreme temperature variations are encountered.
- Water-Based PSAs: Water-based PSAs emerged as an environmentally friendly alternative to solvent-based adhesives. They are used in applications where low VOC emissions are essential.
- Microsphere-enhanced PSAs were introduced to PSA formulations to provide controlled adhesion and repositionability. These adhesives are used in applications like removable labels and notes.
- Nanotechnology: Recent advancements in nanotechnology have led to the development of nanostructured PSA materials, offering enhanced adhesive properties at the nanoscale.
- Smart PSAs: Researchers have been exploring the integration of functionalities into PSAs, such as electrical conductivity, sensing capabilities, and self-healing properties.
- Biodegradable PSAs: With a growing emphasis on sustainability, biodegradable and compostable PSAs have gained attention, offering eco-friendly alternatives for various applications.
Throughout its evolution, PSA technology has created a wide range of products, including tapes, labels, decals, medical dressings, automotive tapes, and more. The versatility, ease of use, and adaptability of PSAs have made them an essential component in various industries, from consumer goods to industrial applications. Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to push the boundaries of what PSA can achieve, leading to even more innovative applications in the future.
How does PSA maintain its adhesive properties under different temperature and humidity conditions?
PSA stands for Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive, and it is a type of adhesive that remains tacky and adheres to surfaces under the application of light pressure. PSA’s unique properties that allow it to maintain its adhesive properties under different temperature and humidity conditions are attributed to its formulation and molecular structure. Here’s how PSA achieves this:
- Viscoelastic Properties: PSA exhibits a viscoelastic nature, exhibiting viscous (flow-like) and elastic (recovery) behaviors under stress. This property enables it to conform to the irregularities of the surfaces it adheres to, creating a large contact area contributing to its adhesion strength. This property remains relatively unaffected by changes in temperature and humidity.
- Soft and Tacky: PSAs are formulated to be smooth and tacky at room temperature. This tackiness results from the adhesive molecules having a certain degree of mobility even in their solid state. This molecular mobility enables the adhesive to interact effectively with surfaces, allowing for adhesion. These soft and tacky characteristics remain stable over various temperatures and humidities.
- Microscopic Interactions: PSA molecules have functional groups that interact with the surface they’re applied to through intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, and dipole-dipole interactions. These interactions are relatively weak but collectively contribute to adhesion. Changes in temperature and humidity typically don’t significantly impact these molecular interactions.
- Thermoplastic Behavior: Many PSAs have a thermoplastic behavior, which means they soften when heated and harden when cooled. This characteristic can help the adhesive maintain its conformability and adhesion properties under different temperature conditions. Even if the glue softens, it usually keeps its tackiness to the point of failing.
- Coating and Backing Materials: The backing material used for PSA tapes or films also plays a role in maintaining adhesive properties. The backing can influence the adhesive’s resistance to temperature and humidity. Some approvals are chosen for their ability to prevent moisture diffusion and provide thermal stability to the adhesive layer.
- Formulation and Chemistry: Manufacturers can adjust the formulation of PSAs to optimize their performance under specific conditions. This might involve incorporating additives that enhance stability against temperature and humidity variations.
It’s important to note that while PSAs are designed to maintain their adhesive properties under various conditions, extreme temperatures or high humidity can still affect their performance over time. In some instances, prolonged exposure to such conditions might lead to reduced adhesion or other performance issues. Therefore, it’s advisable to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for specific temperature and humidity ranges for optimal adhesive performance.
What are the safety considerations when dealing with Pressure Sensitive Adhesive products?
Dealing with Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) products requires careful attention to safety to prevent accidents, exposure, and potential health risks. Here are some essential safety considerations when working with PSA products:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, safety glasses, and, if necessary, respiratory protection. The specific PPE required can depend on the type of PSA, its composition, and the level of exposure.
- Ventilation:Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize the inhalation of adhesive fumes or vapors. If working in a confined space or an area with poor ventilation, consider using respiratory protection.
- Skin Contact:Avoid direct skin contact with PSA products. Use gloves to protect your hands from contact with the adhesive. If skin contact occurs, wash the affected area with soap and water.
- Eye Protection:Wear safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from accidental splashes or contact with adhesive.
- Avoid Ingestion:Do not eat, drink, or smoke in areas where PSA products are used. Wash your hands thoroughly before eating or touching your face.
- Storage:Store PSA products in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper storage conditions.
- Handling and Disposal:Handle PSA products carefully to avoid spills and leaks. Use appropriate containers and tools for handling and dispensing the adhesive. Dispose of waste materials according to local regulations and guidelines.
- Fire Safety:Some PSA products may be flammable. Keep them away from open flames, sparks, and sources of ignition.
- Chemical Compatibility:Be aware of the compatibility of PSA products with other materials. Some adhesives may react with specific substrates or chemicals, leading to undesirable outcomes.
- First Aid:Familiarize yourself with the appropriate first aid measures in case of accidental exposure or ingestion. Have an eye wash station and a first aid kit readily available.
- Training and Education:Ensure that individuals working with PSA products are trained in handling, storage, and safety procedures. This includes understanding the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheet (SDS) the manufacturer provides.
- Emergency Preparedness:Have an emergency plan in place in case of spills, leaks, or accidents involving PSA products. This should include procedures for containment, cleanup, and evacuation if necessary.
- Avoid Mixing Products:Do not mix different types or brands of adhesives unless specified by the manufacturer. Mixing can lead to unpredictable and potentially hazardous reactions.
- Health Concerns:Some people may be sensitive or allergic to specific adhesive components. If you experience any adverse reactions, such as skin irritation or respiratory discomfort, discontinue use and seek medical attention if necessary.
Remember that the safety considerations can vary based on the specific type of PSA product and its intended application. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and the product’s SDS for detailed safety information.
Which industries are still exploring innovative applications of Pressure Sensitive Adhesives?
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) are versatile materials that have applications in various industries. As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, several sectors continue to explore innovative applications of PSAs. Please note that developments in this field might have occurred since then. Some industries where innovative applications of PSAs are being studied include:
1.Medical and Healthcare:PSAs are used in devices like bandages, wound dressings, medical tapes, and wearable sensors. Researchers are exploring new ways to integrate PSAs into advanced wound care products, drug delivery systems, and wearable medical devices.
2.Automotive Industry:In the automotive sector, PSAs are used for applications like attaching trim, bonding interior components, and securing vehicle emblems. The economic benefits include reduced assembly time, lower manufacturing costs, and potential weight savings compared to traditional mechanical fasteners.
3.Healthcare and Medical Devices:PSAs play a significant role in medical devices, wound dressings, and transdermal drug delivery systems. Economic implications include reduced medical procedure times, improved patient comfort, and potentially lower healthcare costs due to efficient and less invasive applications.
4.Electronics and Technology:PSAs are used in electronics for attaching components, bonding displays, and securing batteries. The economic impact includes streamlined assembly processes, potentially lower defect rates, and improved design flexibility.
5.Construction and Building Materials:PSAs are employed in the construction industry for applications like mounting mirrors, attaching insulation materials, and bonding flooring components. Economic implications include reduced installation time, enhanced durability, and potential cost savings in labor and materials.
6.Consumer Goods and Retail:PSAs are used in various consumer products, such as tapes, adhesive hooks, and decals. The economic benefits include efficient packaging, ease of use for consumers, and opportunities for product differentiation.
7.Aerospace and Defense:In the aerospace sector, PSAs are used in interior components, aircraft insulation, and protective films. Economic implications include potential weight reduction, improved maintenance processes, and reduced repair downtime.
8.Renewable Energy:PSAs are applied in the renewable energy sector for attaching solar panels, wind turbine components, and other renewable energy systems. Economic benefits include faster installation, potentially reduced maintenance costs, and increased adoption of renewable energy technologies.
It’s important to note that while there are many potential economic benefits to using PSAs in various sectors, there can also be challenges, such as material costs, quality control, and the need for proper substrate preparation to ensure adequate bonding. Additionally, the economic implications may change as technology and adhesive formulations evolve.
How might future advancements in adhesive technology further enhance the convenience of PSA in our lives?
Future advancements in adhesive technology could significantly enhance the convenience and versatility of Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) in various aspects of our lives. Here are some potential ways in which these advancements might occur:
- Stronger and Thinner Adhesives: Advancements in molecular engineering could lead to more robust and thinner adhesives. This would allow for more secure bonding between surfaces while reducing the overall bulkiness of adhesive applications.
- Enhanced Durability: Future adhesives could be designed to withstand extreme conditions such as high temperatures, humidity, and chemical exposure. This would extend the range of applications where PSAs can be used, including in automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings.
- Instant Bonding: Faster curing and instant bonding capabilities could be achieved through advancements in chemical formulations. This would eliminate the need for prolonged clamping or waiting periods, making assembly processes more efficient.
- Repositionable and Removable Adhesives: Improved repositionable adhesives could allow users to adjust the position of bonded items without damaging surfaces. Similarly, enhanced removable adhesives could leave no residue or damage upon removal, making them more user-friendly.
- Intelligent and Responsive Adhesives: Adhesives could be developed to respond to specific stimuli, such as temperature, pressure, or light. This could lead to applications like self-healing materials or adhesives that change their properties based on environmental conditions.
- Bio-Inspired Adhesives: Researchers continually study the adhesion mechanisms found in nature, such as gecko feet and mussel adhesive proteins. Future PSAs might replicate these natural principles to create adhesives with exceptional sticking power and versatility.
- Eco-Friendly Formulations: As environmental concerns grow, there could be a focus on developing PSAs that are biodegradable, made from renewable resources, or have minimal impact on the environment throughout their lifecycle.
- Integration with Electronics: Adhesives that are conductive or have other electronic properties could facilitate the integration of electronic components in various applications, such as wearable devices, flexible electronics, and medical sensors.
- Customizable Adhesive Properties: Advances in materials science and manufacturing techniques could allow for tailored adhesive properties, such as specific levels of tackiness, flexibility, and shear strength. This could make adhesives more adaptable to diverse applications.
- 3D Printing with Adhesives: Combining 3D printing technology with adhesive properties could create intricate and customized structures that are both mechanically stable and adhesive.
- Medical and Healthcare Applications: Future PSAs could be crucial in medical devices, wound care, and drug delivery systems, offering gentle yet secure adhesion to skin and biological tissues.
- Advanced Packaging Solutions: PSAs could continue revolutionizing packaging by enabling easy-to-open seals, resealable closures, and more sustainable packaging solutions.
Overall, future advancements in adhesive technology have the potential to revolutionize how we interact with materials and objects in our daily lives, offering improved convenience, durability, and versatility in various applications.