Silicone Sealant

Silicone sealants, with their versatile properties and exceptional adhesive capabilities, have revolutionized various industries and applications, from construction and automotive to electronics and healthcare. The remarkable potential of silicone sealants lies in their ability to create reliable and durable bonds and in their resistance to extreme temperatures, moisture, and other environmental factors.
This article delves into the extensive uses and insights surrounding silicone sealants, exploring their diverse applications, composition, and the pivotal role they play in enhancing product performance and structural integrity. By unraveling the multifaceted aspects of silicone sealants, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these remarkable compounds continue to unlock new dimensions of innovation across industries.
What Makes Silicone Sealants Unique?
Silicone sealants are adhesive materials commonly used for sealing joints, gaps, and seams in various applications. They are unique due to their composition, properties, and versatility. Here are some key features that make silicone sealants stand out:
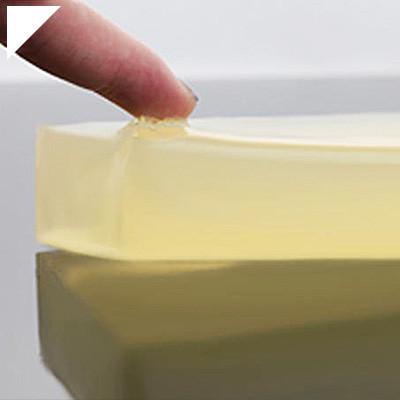
- Flexibility and Elasticity: Silicone sealants remain flexible and elastic even after they cure, meaning they can withstand movement and vibrations without cracking or losing effectiveness. This property is precious in applications with constant expansion, contraction, or other activity.
- Temperature Resistance: Silicone sealants have excellent resistance to a wide range of high and low temperatures. They can handle extreme heat and cold without deteriorating, making them suitable for outdoor and industrial applications.
- Waterproof and Weatherproof: Silicone sealants are known for their superior water resistance. Once cured, they create a waterproof barrier that prevents water, moisture, and some chemicals from penetrating gaps and joints. This property makes them ideal for sealing windows, doors, and other areas exposed to moisture.
- UV Resistance: Many silicone sealants are formulated to resist UV radiation, which helps them maintain their color and flexibility when exposed to sunlight. This feature is crucial for outdoor applications where prolonged sun exposure is a factor.
- Chemical Stability: Silicone sealants exhibit high resistance to chemicals, oils, solvents, and various environmental pollutants. This makes them suitable for use in areas where exposure to chemicals or pollutants is likely.
- Non-Corrosive: Silicone sealants are non-corrosive and do not react with most building materials, metals, or other substances they come into contact with. This property prevents damage to surfaces and materials they are applied to.
- Longevity: Properly used and maintained silicone sealants can have a long lifespan, often many years, without significant degradation. This makes them a reliable choice for sealing projects that require durability.
- Ease of Application: Silicone sealants are available in various forms, such as tubes, cartridges, and squeeze bottles, and can be easily applied using a caulking gun or by hand. They adhere well to various materials, including glass, metal, plastic, wood, and ceramics.
- Transparency and Aesthetics: Silicone sealants are available in precise formulations. These can be particularly useful when a seamless and aesthetically pleasing finish is desired, such as in glass or acrylic applications.
- Versatility: Silicone sealants are used in various applications, including construction, automotive, electronics, plumbing, and more. Their adaptability and ability to perform in diverse environments contribute to their popularity.
It’s important to note that while silicone sealants have numerous benefits, they also have some limitations. For instance, they may not adhere to certain surfaces like porous materials or characters already coated with certain sealants. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and choosing the appropriate silicone sealant for your specific application is recommended to ensure the best results.
What Are Silicone Sealants Composed Of?
Silicone sealants are a type of adhesive or sealant that are primarily composed of silicone polymers. These polymers are synthetic materials derived from silicon, a chemical element found in sand and quartz, and are known for their flexibility, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. The composition of silicone sealants can vary slightly based on the specific formulation and intended use, but the essential components include:
- Silicone Polymers:The primary component of silicone sealants is silicone polymers, usually derived from siloxane monomers. These polymers provide the adhesive and sealing properties of the product.
- Fillers:Fillers are added to the silicone sealant formulation to improve its properties, such as reinforcement, viscosity control, and color stability. Joint fillers include calcium carbonate, silica, and various minerals.
- Cross-Linking Agents:Silicone sealants are often moisture-curing, meaning they harden and form a seal when they come into contact with atmospheric moisture. Cross-linking agents are added to facilitate this curing process by promoting the cross-linking of polymer chains.
- Curing Catalysts:Curing catalysts accelerate the curing reaction, helping the silicone sealant harden more quickly and effectively.
- Modifiers and Additives:Additional ingredients can be included to enhance specific properties of the sealant, such as UV resistance, heat resistance, flame resistance, and flexibility. Additives can also affect the sealant’s texture, adhesion, and workability.
- Solvents:Some formulations of silicone sealants might contain solvents to help adjust the viscosity and aid in application. However, solvent-containing formulations are becoming less common due to environmental and health concerns.
- Pigments:Pigments are added to silicone sealants to provide color. This is especially important for adhesives used in construction or automotive applications where aesthetics are essential.
It’s worth noting that various types of silicone sealants are designed for specific applications, such as high-temperature sealants, waterproofing sealants, aquarium sealants, automotive sealants, and more. The particular formulation and additives can vary based on the intended use and the desired properties of the adhesive. Always refer to the product’s technical data sheet or manufacturer’s guidelines for precise information about its composition and recommended uses.
What Sets Silicone Sealants Apart From Other Sealant Types?
Silicone sealants are a type of adhesive sealant that is widely used for various sealing and bonding applications. They are distinct from other types of sealants due to several key characteristics:
- Flexibility and Durability:Silicone sealants are known for their excellent flexibility and durability over a wide temperature range. They can withstand extremely high and low temperatures without losing their sealing properties. This makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Water Resistance:Silicone sealants are inherently water-resistant. They can form a watertight seal that prevents water penetration, making them ideal for sealing around sinks, showers, windows, and other areas exposed to moisture.
- Chemical Resistance:Silicone sealants have good resistance to various chemicals, oils, and solvents, making them suitable for use in environments where exposure to these substances is a concern.
- UV Resistance:High-quality silicone sealants often resist ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which helps them maintain their integrity and prevent degradation when exposed to sunlight. This makes them suitable for outdoor applications.
- Adhesion to Multiple Surfaces:Silicone sealants can adhere well to a wide range of surfaces, including glass, metal, ceramics, plastics, and certain types of wood. This versatility makes them useful for various bonding and sealing tasks.
- Non-Corrosive:Silicone sealants are non-corrosive to most common building materials, which means they won’t cause damage to surfaces they come into contact with.
- Low Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):Many silicone sealants are formulated with low levels of VOCs, contributing to better indoor air quality and reduced environmental impact.
- Ease of Application:Silicone sealants are available in various forms, including cartridges, squeeze tubes, and caulking guns, making them easy to apply. They can be used for both minor touch-ups and larger sealing projects.
- Long Shelf Life:Silicone sealants typically have a longer shelf life than some other sealant types, retaining their effectiveness even after extended storage periods.
It’s important to note that while silicone sealants have many advantages, some applications may have better choices. For example, they might not adhere well to certain porous surfaces like untreated wood or certain plastics. In some specialized cases, other types of sealants like polyurethane or acrylic may offer better performance. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project when selecting the appropriate sealant type.
What Are the Primary Benefits of Using Silicone Sealants?
Silicone sealants are versatile and widely used materials known for their flexibility, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. Here are some primary benefits of using silicone sealants:
- Flexibility: Silicone sealants remain flexible even after curing, allowing them to accommodate movement and expansion in materials without cracking or losing their effectiveness. This makes them ideal for sealing joints and structural gaps that experience temperature fluctuations or vibrations.
- Water Resistance: Silicone sealants are highly resistant to water, making them suitable for sealing in wet environments such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor applications. They can withstand prolonged exposure to moisture without degrading or losing their sealing properties.
- Weather Resistance: Silicone sealants exhibit excellent resistance to UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and weathering. This makes them a preferred choice for interior and exterior applications, as they can maintain their integrity and sealing capabilities over time.
- Adhesion: Silicone sealants adhere well to various substrates, including glass, metal, ceramic, plastic, and building materials. This adhesion contributes to their effectiveness in creating watertight and airtight seals.
- Longevity: Due to their durability and resistance to degradation from sunlight, moisture, and temperature changes, silicone sealants typically have a longer service life compared to other types of adhesives. This can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs in the long run.
- Non-Toxic and Low Odor: Silicone sealants are generally non-toxic after curing and emit low odor levels during the curing process. This makes them suitable for use in enclosed or indoor environments without causing significant discomfort to occupants.
- Transparency and Aesthetics: Silicone sealants come in various formulations, including transparent options. This allows for more discreet sealing in applications with essential aesthetics, such as glass-to-glass or glass-to-metal joints.
- Electrical Insulation: Silicone sealants possess good electrical insulating properties, making them suitable for sealing around electrical components and connections. They can help protect against moisture and contaminants that might otherwise compromise electrical systems.
- Chemical Resistance: Silicone sealants resist many chemicals, including solvents and cleaning agents. This property can be beneficial in environments where chemical exposure is a concern.
- Ease of Application: Silicone sealants are available in various forms, including cartridges and tubes, and they are relatively easy to apply using standard caulking guns. They also have a reasonable working time before curing, allowing for adjustments to be made during the application process.
It’s important to note that while silicone sealants offer these advantages, they may only be suitable for some applications. Depending on the specific requirements of your project, you should consider factors such as the type of substrate, the anticipated movement, and the intended exposure conditions when selecting a sealant type.
How are Silicone Sealants Used in Construction?
Due to their excellent adhesive and sealing properties, silicone sealants are versatile and widely used materials in the construction industry. They are typically based on silicone polymers and are available in various formulations, including one-part, two-part, and neutral-cure options. Here’s how silicone sealants are used in construction:
- Sealing Joints and Gaps:Silicone sealants are commonly used to fill joints and gaps in various building components, such as windows, doors, curtain walls, and expansion joints. These sealants help prevent air and water infiltration, providing a watertight and airtight barrier. They can accommodate movement caused by thermal expansion and contraction without losing their adhesion.
- Weatherproofing:Silicone sealants are weather-resistant and can withstand exposure to harsh environmental conditions, including UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and moisture. This makes them suitable for exterior applications where long-term durability is essential.
- Glazing Applications:In glazing systems, silicone sealants secure glass panels to frames, creating a solid and secure bond. These sealants ensure structural integrity and prevent water leakage while allowing some movement between the glass and frame.
- Concrete and Masonry Joints:Silicone sealants can seal joints and cracks in concrete and masonry structures. They help prevent water penetration and the deterioration of these materials over time. Silicone sealants can also be used in expansion and control joints in concrete to accommodate movement.
- Interior Applications:Silicone sealants are used indoors, such as in bathrooms and kitchens. They are resistant to mold and mildew growth, making them suitable for sealing joints around sinks, bathtubs, and other moisture-prone areas.
- Fire-Resistant Sealants:Some silicone sealants are formulated to provide fire resistance. These sealants are used when fire containment is crucial, such as sealing gaps and joints in fire-rated walls and floors.
- Acoustic Sealants:Silicone sealants can contribute to sound insulation by sealing gaps and joints in walls, ceilings, and floors. This helps reduce the transmission of sound between different areas of a building.
- Aesthetic Applications:Silicone sealants are available in various colors to match the surrounding surfaces. This makes them suitable for aesthetic applications where appearance is essential, such as sealing joints in architectural features or decorative elements.
- Industrial Applications:Silicone sealants are also used in industrial settings for sealing joints and connections in machinery, equipment, and other industrial components.
Proper surface preparation is essential for achieving good adhesion when using silicone sealants in construction. This involves cleaning and priming the surfaces before applying the adhesive. Additionally, selecting the appropriate type of silicone sealant for the specific application is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
How Do Silicone Sealants Contribute to Waterproofing in Construction?
Silicone sealants are widely used in construction for their excellent waterproofing properties and versatility. They play a crucial role in preventing water infiltration and ensuring the integrity of building structures. Here’s how silicone sealants contribute to waterproofing in construction:
- Flexible and Elastic Properties:Silicone sealants are known for their high flexibility and elasticity. This means they can accommodate the movement and expansion of building materials caused by temperature changes, settling, and vibrations without losing their sealing properties. This flexibility helps prevent cracks and gaps from forming, which could otherwise allow water to seep into the structure.
- Adhesion:Silicone sealants have strong adhesion to various building materials, including glass, metal, concrete, wood, and plastics. This strong bond creates a watertight barrier between different materials, ensuring water cannot penetrate through joints or seams.
- Impermeability:Silicone sealants are inherently resistant to water penetration. They form a cohesive, non-porous layer that prevents water molecules from passing through the adhesive. This quality is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of building components and preventing water-related damage, such as mold growth, corrosion, and deterioration.
- Sealing Joints and Cracks:Construction projects involve various joints, gaps, and seams where water could infiltrate. Silicone sealants are applied to these areas to fill gaps and create a continuous barrier against water intrusion. They seal joints around windows, doors, roofs, expansion joints, and other critical areas.
- Durability:Silicone sealants are known for their long-term durability. They resist UV radiation, extreme temperatures, moisture, and other environmental factors that can degrade other materials over time. This durability ensures the sealant maintains its waterproofing capabilities throughout the building’s lifespan.
- Easy Application:Silicone sealants come in various forms, including cartridges, tubes, and pre-formed strips. They can be easily applied using a caulking gun, making them convenient for professional construction workers and DIY enthusiasts. The ease of application ensures that sealants are correctly placed in areas prone to water infiltration.
- Aesthetic Appeal:Silicone sealants are available in various colors, allowing builders to choose an adhesive that matches the appearance of the surrounding materials. This ensures that the bond not only provides waterproofing but also contributes to the overall aesthetics of the building.
- Low Maintenance:Once silicone sealants are correctly applied and cured, they require minimal maintenance. Their resistance to water, chemicals, and weathering means they remain effective without frequent reapplication or repairs.
How are Silicone Sealants Applied for Expansion Joint Sealing?
Applying silicone sealants for expansion joint sealing involves a systematic process to ensure proper adhesion, flexibility, and durability. Expansion joints are gaps designed to accommodate the movement of materials due to temperature changes, settling, or other factors. Silicone sealants are commonly used because of their flexibility, weather resistance, and adhesive properties. Here’s a general guide on how to apply silicone sealants for expansion joint sealing:
Materials and Tools Needed:
- Silicone Sealant: Choose a high-quality silicone sealant specifically designed for expansion joints.
- Caulking Gun: To dispense the sealant accurately.
- Utility Knife: For preparing the joint and trimming excess adhesive.
- Backer Rod: Foam or other flexible material to support the sealant.
- Cleaner: To clean the joint before applying the adhesive.
- Masking Tape: To create clean edges and prevent excess sealant from spreading.
- Isopropyl Alcohol: For cleaning tools and surfaces.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Surface Preparation:
- Clean the expansion joint thoroughly. Remove dirt, debris, loose materials, and old sealant using a brush or vacuum.
- Use isopropyl alcohol or a recommended cleaner to ensure the joint is free from oils and contaminants.
- Backer Rod Installation:
- If the expansion joint is wide or deep, consider installing a backer rod before applying the sealant. The backer rod provides support and controls the depth of the sealant.
- Insert the backer rod into the joint, ensuring it fits snugly but not too tightly. It should be about 1/8 to 1/4 inch below the surface.
- Masking and Taping:
- Apply masking tape along the edges of the joint to create clean lines and prevent the sealant from spreading to unwanted areas.
- Applying the Silicone Sealant:
- Load the silicone sealant cartridge into the caulking gun and cut the tip of the nozzle at a 45-degree angle to achieve the desired bead size.
- Start applying the sealant to the joint, making sure it fills the joint and makes good contact with the sides.
- Use steady and even pressure on the caulking gun while moving it along the joint.
- If a backer rod is used, ensure the sealant slightly overlaps the rod.
- Smoothing and Tooling:
- Immediately after applying the sealant, use a tool (often a gloved finger or a specialized tool) to smooth and shape the sealant into the joint.
- This step ensures a proper seal, good adhesion, and a neat appearance.
- Removing Excess Sealant:
- Once the sealant is tooled, carefully remove the masking tape before the sealant starts to cure. This prevents the video from getting stuck in the sealant.
- Curing Time:
- Silicone sealants have a curing time indicated on the product label. Allow the sealant to cure undisturbed for the recommended time before subjecting it to movement or exposure to water.
Remember to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for your specific silicone sealant. Proper application is crucial for achieving an effective and long-lasting seal in expansion joints.
How Do Silicone Sealants Facilitate Window and Door Installations?
Silicone sealants are crucial in facilitating window and door installations by providing a secure and weather-resistant seal between the frames and the surrounding building structure. Here’s how silicone sealants are used in this context:
1.Weatherproofing:Silicone sealants are highly resistant to moisture and outdoor elements. When used around windows and doors, they create a barrier that prevents water, air, and drafts from entering the building. This is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment and preventing energy loss.

2.Adhesion:Silicone sealants adhere well to various surfaces, including glass, metal, wood, and masonry. This allows them to securely bond the window or door frame to the building structure, ensuring stability and structural integrity.
3.Flexibility:Buildings can experience slight movements due to temperature changes, settling, or other factors. Silicone sealants have excellent flexibility, which allows them to accommodate these movements without cracking or losing their sealing properties. This helps prevent gaps from forming around the window or door frame over time.
4.Expansion and Contraction:Silicone sealants have a high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning they can expand and contract with temperature changes without losing their effectiveness. This is particularly important for windows and doors, as they can be exposed to varying temperatures and weather conditions.
5.Durability:High-quality silicone sealants are designed to withstand UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and various environmental conditions. This durability ensures that the seal remains effective over an extended period, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacements.
6.Aesthetics:Silicone sealants are available in various colors, including transparent and translucent options. This allows for a more aesthetically pleasing finish around windows and doors, as the sealant can blend with the surrounding materials.
7.Easy Application:Silicone sealants are typically available in cartridges that can be easily dispensed using a caulking gun. This makes them relatively straightforward to apply, ensuring installers can create a consistent and effective seal.
8.Sound Insulation:Silicone sealants can contribute to sound insulation by filling gaps and preventing the transmission of noise from the outside to the interior of the building.
9.Versatility:Silicone sealants can be used for various sealing and bonding applications beyond windows and doors. This includes sealing joints, gaps, and cracks in other building parts.
Silicone sealants provide a reliable and long-lasting solution for sealing windows and doors during installation. They offer a combination of weather resistance, adhesion, flexibility, and durability, contributing to the overall performance and energy efficiency of a building. Properly applied silicone sealants help create a tight, secure seal that minimizes air and water infiltration, reduces energy costs, and enhances the lifespan of windows and doors.
Where Can Silicone Sealants Be Applied?
Silicone sealants are versatile products commonly used for sealing and bonding a wide range of materials. They have excellent adhesive and sealing properties and resistance to moisture, temperature variations, and UV radiation. Here are some typical applications for silicone sealants:
- Kitchen and Bathroom: Silicone sealants are often used to seal joints and gaps around sinks, faucets, showers, bathtubs, and countertops. They prevent water penetration and help prevent mold growth.
- Windows and Doors: Silicone sealants can seal gaps around windows and doors to prevent drafts, water leaks, and air infiltration.
- Construction and Building: Silicone sealants are used in various construction applications, such as sealing expansion joints, connecting different building materials, filling gaps in masonry, and weatherproofing.
- Automotive: Silicone sealants are used in the automotive industry for sealing windows, windshields, taillights, and other joints to prevent water and air leaks.
- Electronics: Silicone sealants can protect against moisture and dust in electronic components, connectors, and outdoor electrical installations.
- Plumbing: They can seal fixtures, pipe joints, and connections to prevent leaks.
- HVAC Systems: Silicone sealants seal joints and connections in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to prevent air and moisture leakage.
- Glass and Mirrors: Silicone sealants can bond and seal glass panels, mirrors, and other components.
- Crafts and Hobbies: Silicone sealants are often used in DIY projects, skills, and hobbies for bonding materials like glass, plastic, metal, and ceramics.
- Marine Applications: Due to their resistance to water and UV radiation, silicone sealants are used in marine environments to seal joints, gaps, and seams in boats and other marine structures.
- Roofing: Silicone sealants can be used for sealing roof penetrations, flashing, and seams to prevent water leaks.
- Automated Manufacturing: Silicone sealants are used in industrial settings for bonding and sealing components in automated manufacturing processes.
It’s important to note that different silicone sealants are designed for specific applications, such as high-temperature ones for applications involving extreme heat and aquarium-safe silicone sealants for sealing fish tanks. Always choose the appropriate type of silicone sealant for your specific application to ensure proper adhesion and performance.
Where Are High-Temperature Silicone Sealants Utilized?
High-temperature silicone sealants are used in various industrial and commercial applications where the sealing material needs to withstand elevated temperatures. These sealants are designed to maintain their physical properties, adhesion, and effectiveness at temperatures much higher than regular silicone sealants can handle. Some common areas where high-temperature silicone sealants are utilized include:
- Automotive Industry: High-temperature silicone sealants are used in the automotive sector to seal various engine components, exhaust systems, and other parts exposed to high temperatures generated by combustion and engine operation.
- Aerospace Industry: Aerospace applications involve extreme temperature fluctuations due to atmospheric re-entry, combustion, and the heat generated during space travel. High-temperature silicone sealants seal joints and components in spacecraft, satellites, and other aerospace vehicles.
- Industrial Ovens and Furnaces: In industries such as manufacturing, food processing, and ceramics, high-temperature silicone sealants are used to seal joints and gaps in industrial ovens, furnaces, and kilns. These sealants help maintain proper insulation and prevent heat leakage.
- High-Performance Electronics: Some electronic components generate significant heat during operation. High-temperature silicone sealants can encapsulate and seal these components, ensuring their protection and preventing the ingress of moisture or contaminants.
- Power Generation: Both conventional and renewable energy sources can generate high temperatures in power plants. High-temperature silicone sealants seal connections, joints, and gaskets in boilers, turbines, and exhaust systems.
- Exhaust Systems: Automotive, marine, and industrial exhaust systems require sealants that can withstand the high temperatures produced by combustion. High-temperature silicone sealants seal joints and connections in exhaust pipes and manifolds.
- High-Temperature Pipelines: Industries like oil and gas often have pipelines that transport materials at high temperatures. Silicone sealants seal joints, connections, and fittings in these pipelines.
- Fireplace and Stove Sealing: High-temperature silicone sealants seal gaps and joints in fireplaces, wood-burning stoves, and other heating appliances. These sealants prevent heat and gas leakage and ensure safe operation.
- Gaskets and Seals: High-temperature silicone sealants can be used to create custom gaskets and seals for specific applications, especially when traditional gasket materials fail due to high temperatures.
- High-Performance Sealing: Generally, any application that involves sealing at elevated temperatures may benefit from using high-temperature silicone sealants. These sealants provide durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat, making them suitable for various specialized applications.
It’s important to note that the exact specifications and suitability of a high-temperature silicone sealant for a particular application depend on factors such as the temperature range, chemical compatibility, and physical properties required for the specific environment. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations before selecting and applying a high-temperature silicone sealant.
Where Are Flexible Silicone Sealants Preferred over Rigid Adhesives?
Flexible silicone sealants are preferred over rigid adhesives in various applications where movement, vibration, or expansion and contraction of materials are expected. The flexibility of silicone sealants allows them to accommodate these movements without cracking or losing adhesion, making them suitable for a wide range of scenarios. Here are some areas where flexible silicone sealants are preferred over rigid adhesives:
- Construction and Building:Silicone sealants are commonly used for sealing joints, gaps, and cracks in buildings, windows, doors, and various surfaces. Buildings experience thermal expansion and contraction due to temperature variations, settling, and other structural changes. Flexible silicone sealants can withstand these movements without losing their adhesion or creating gaps that can lead to water leakage, drafts, or other issues.
- Automotive Industry:In automobiles, silicone sealants are used for sealing gaps and joints in various parts of the vehicle. Cars and other vehicles undergo constant vibrations and movements while in operation, and rigid adhesives would likely crack under these conditions. Flexible silicone sealants ensure a durable, watertight seal that can withstand mechanical stress.
- Electronics and Electrical Components:Flexible silicone sealants protect electronics and electrical components from moisture, dust, and environmental factors. These sealants are applied to seal connections, joints, and device gaps. The flexibility of silicone ensures that the seal remains intact even when the components experience slight movements or vibrations.
- Marine and Aerospace:Both marine and aerospace industries require sealants that can withstand extreme conditions, including changes in temperature, pressure, and movement. Flexible silicone sealants are used in these industries to seal joints, connections, and seams in equipment, vessels, and aircraft.
- HVAC Systems:Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems involve a lot of temperature fluctuations and vibration. Flexible silicone sealants seal gaps and joints in HVAC ducts and equipment, ensuring energy efficiency and preventing air leaks.
- Plumbing:In applications such as sealing around pipes and fixtures, silicone sealants provide a waterproof and flexible barrier that can accommodate small pipe shifts and prevent leaks.
- Glass and Glazing:Silicone sealants are often used to seal glass panels in windows and curtain walls. The flexibility of the adhesive allows it to accommodate the slight movement and thermal expansion of the glass without compromising the structural integrity of the installation.
- Food and Medical Industry:Silicone sealants are used in environments where cleanliness is essential, such as food and medical facilities. They seal joints and gaps in equipment and surfaces while withstanding the cleaning processes and maintaining a hygienic environment.
Overall, flexible silicone sealants are preferred when there is a need for a durable and long-lasting seal that can adapt to movement, vibration, and temperature changes. Their ability to maintain adhesion under these conditions makes them versatile in various industries and applications.
Where Do Electronics and Aerospace Industries Employ Silicone Sealants?
Due to their unique properties, the electronics and aerospace industries employ silicone sealants for various purposes. Silicone sealants are versatile materials that offer excellent adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to temperature extremes, moisture, and chemicals. Here are some typical applications of silicone sealants in these industries:
Electronics Industry:
- Encapsulation and Potting:Silicone sealants are used to encapsulate and pot electronic components to protect them from environmental factors like moisture, dust, and vibration. This is particularly important in harsh operating conditions.
- Bonding and Sealing:Silicone sealants are used to bond and seal components like connectors, cables, and housing to prevent moisture ingress, which can lead to corrosion and malfunctions.
- Thermal Management:Silicone-based thermal interface materials (TIMs) improve heat dissipation between electronic components and heatsinks, ensuring efficient cooling and prolonging component life.
- Gasketing:Silicone sealants create gaskets for electronic enclosures, providing a barrier against moisture and dust. They also aid in reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI).
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Protection:Silicone sealants can protect sensitive PCBs from moisture, dust, and other contaminants, enhancing the reliability and longevity of electronic devices.
Aerospace Industry:
- Aircraft Sealing:Silicone sealants seal joints, seams, and gaps in aircraft structures, such as fuselages, wings, and access panels. They provide airtight and watertight seals, helping to maintain the integrity of the aircraft’s design.
- Window and Windshield Bonding:Silicone sealants bond and seal aircraft windows and windshields. They provide optical clarity, weather resistance, and structural support.
- Cable and Wire Sealing:In aerospace applications, silicone sealants protect cables and wires from moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
- Avionics Protection:Avionics components, which include electronic systems for navigation, communication, and control, are often sealed with silicone to protect them from the harsh conditions of flight.
- Rocket and Spacecraft Sealing:Silicone sealants play a crucial role in sealing joints, connectors, and components in rockets and spacecraft to prevent leaks and maintain the vehicles’ integrity in the space vacuum.
- Engine Sealing:Aircraft engines use silicone sealants to seal various components and prevent leakage of fluids and gasses.
Both industries value silicone sealants for their reliability, durability, and ability to withstand extreme conditions. The properties of silicone sealants make them well-suited for applications where sealing, bonding, and protection are critical to the performance and longevity of electronic and aerospace equipment.
How Should Surfaces Be Prepared Before Applying Silicone Sealants?
Proper surface preparation is essential for achieving a strong and durable bond when applying silicone sealants. The surface preparation quality directly affects the sealant’s adhesion and longevity. Here’s how surfaces should be prepared before applying silicone sealants:
1.Clean the Surface:Ensure the surface is clean and free from dirt, dust, grease, oil, rust, and other contaminants. Use a suitable cleaning agent that doesn’t leave residues or affect the substrate.

2.Degrease:If the surface has grease or oil residues, use a degreasing agent to clean the area thoroughly. This ensures that the silicone sealant can adhere properly to the substrate.
3.Remove Old Sealant:If old sealant or adhesive is present, obliterate it using appropriate tools like scrapers or solvents. Ensure that the surface is clean and smooth after removal.
4.Abrade or Sand:Depending on the substrate material, you may need to rub or sand the surface lightly. This helps create a slightly roughened texture, enhancing the silicone sealant’s adhesion. Be cautious not to damage the substrate.
5.Solvent Cleaning:After sanding, use a solvent appropriate for the substrate (such as isopropyl alcohol) to remove any dust or debris created during the abrasion process. Allow the surface to dry thoroughly before applying the sealant.
6.Priming (if required):Some substrates, like certain metals or plastics, may benefit from a primer to improve adhesion. Consult the sealant manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate primer to use.
7.Masking:If you want to achieve neat and clean lines, especially when working on joints, use masking tape to define the area where the sealant will be applied. This helps to create a clean edge and prevents excess sealant from spreading.
8.Avoid Moisture:Make sure the surface is dry before applying the sealant. Moisture or water can interfere with the curing process and adhesion.
9.Temperature and Humidity:The temperature and humidity of the environment can impact the adhesion and curing of silicone sealants. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for optimal temperature and humidity conditions during application and curing.
10.Read Manufacturer Instructions:Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions on the sealant packaging for specific surface preparation recommendations. Different sealant formulations may have varying requirements.
11.Test Compatibility:If you’re applying silicone sealant to a new or unfamiliar substrate, consider performing a compatibility test on a small, inconspicuous area to ensure the sealant adheres properly and doesn’t react negatively.
Proper surface preparation is a critical step to ensure the effectiveness and longevity of the sealant. Taking the time to prepare the surface correctly will lead to a stronger bond, better adhesion, and a more successful application overall.
What Are the Key Steps for Achieving Proper Sealant Adhesion?
Proper sealant adhesion is essential to ensure the effectiveness and longevity of seals in various applications, such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. Here are the key steps to achieve proper sealant adhesion:
- Surface Preparation:Clean the characters to be sealed thoroughly. Remove all dirt, dust, debris, oils, grease, rust, and old sealant remnants. Use appropriate cleaning agents and techniques based on the material and application, such as solvent wiping, sanding, or abrasive blasting.
- Surface Priming:Sometimes, a primer is necessary to improve adhesion. Primers help promote bonding between the sealant and the substrate, especially on challenging surfaces like metals, plastics, and certain types of stone. Apply the primer according to the manufacturer’s instructions and allow it to dry or cure adequately before applying the sealant.
- Compatibility Testing:Ensure that the sealant is compatible with the substrate materials. Some sealants may interact adversely with specific substrates, leading to poor adhesion or material degradation. Perform compatibility testing on a small, inconspicuous area before full-scale application.
- Select the Right Sealant:Choose a sealant suitable for the specific application and materials. Consider factors such as flexibility, temperature resistance, UV resistance, chemical resistance, and required longevity.
- Application Technique:Apply the sealant using the appropriate method. Standard techniques include caulking, troweling, spraying, or extrusion. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding application temperature, curing time, and recommended thickness.
- Joint Design:Design the joint or gap where the sealant will be appropriately applied. Collective dimensions, depth, and shape play a significant role in achieving good adhesion. The joint should be clean and free from any loose or obstructive materials.
- Proper Tooling:After applying the sealant, use the appropriate tool (such as a caulking gun or trowel) to smooth and shape the sealant. Right tooling ensures that the sealant adheres well to both sides of the joint and reduces the chances of air pockets or voids forming.
- Curing Time:The sealant can cure or dry per the manufacturer’s instructions. Curing times can vary based on the type of sealant, environmental conditions, and joint dimensions. Premature exposure to moisture or stress can negatively affect adhesion.
- Environmental Conditions:Ensure that the application environment meets the requirements for proper adhesion. Factors like temperature, humidity, and moisture levels can influence the curing and bonding process of the sealant.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance:Once the sealant is in place, regularly inspect the sealed area for any signs of degradation, cracking, or loss of adhesion. Perform necessary maintenance to address any issues promptly.
Remember that different sealant types (e.g., silicone, polyurethane, acrylic) and application scenarios may have specific requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and best practices for the sealant and substrate you are working with to achieve the best possible adhesion results.
How Does Cure Time Affect the Performance of Silicone Sealants?
Cure time plays a critical role in determining the performance of silicone sealants. Silicone sealants are widely used for various applications due to their flexibility, durability, and resistance to temperature extremes, moisture, and UV radiation. Here’s how to cure time affects the performance of silicone sealants:
- Initial Adhesion and Handling Strength:During the initial stages of curing, silicone sealants achieve what is known as “handling strength.” This means the sealant forms a skin or surface layer that provides some adhesion and resistance to movement. This is important for preventing the sealant from sagging or flowing out of the joint after application.
- Cohesive Strength Development:As silicone sealants continue to cure, they develop cohesive strength within the material. This strength holds the sealant together and contributes to its ability to withstand stresses and strains without tearing or splitting.
- Complete Cure and Maximum Performance:The full cure of silicone sealants takes time, often ranging from a few hours to several days, depending on factors like temperature, humidity, and the specific formulation of the sealant. During this time, the sealant continues to cross-link and polymerize, resulting in its maximum physical properties. This includes achieving its complete flexibility, adhesion strength, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Flexibility and Movement Resistance:Silicone sealants are known for their excellent flexibility and ability to accommodate joint movement due to temperature changes, structural settling, or other factors. Proper cure time ensures that the sealant has developed the necessary flexibility to handle these movements without cracking or losing adhesion.
- Chemical Resistance and Durability:Longer cure times often contribute to improved chemical resistance and long-term durability of silicone sealants. Adequate curing ensures the adhesive has a stable molecular structure, allowing it to resist degradation from exposure to chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation.
- Resistance to Moisture and Environmental Factors:The complete cure of silicone sealants enhances their ability to repel moisture and resist the growth of mold and mildew. A well-cured sealant forms a barrier that helps prevent water infiltration and subsequent damage.
- Stress Relaxation:Silicone sealants may experience stress relaxation over time, gradually losing some initial stress and strain due to creep and other material behaviors. Adequate cure time helps mitigate this effect, ensuring the sealant maintains its integrity over an extended period.
It’s important to note that the exact cure time required for silicone sealants can vary based on the specific formulation, environmental conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Rushing the curing process by exposing the sealant to extreme conditions or mechanical stress before it’s fully cured can result in compromised performance, reduced adhesion, and decreased durability. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cure time and environmental conditions to achieve the best results with silicone sealants.
What Factors Can Impact the Durability of Silicone Sealants?
The durability of silicone sealants can be influenced by various factors that affect their performance over time. Silicone sealants are commonly used for sealing joints and gaps in a wide range of applications, including construction, automotive, and household uses. Here are some key factors that can impact the durability of silicone sealants:
- Exposure to UV Radiation:Silicone sealants exposed to direct sunlight or UV radiation can experience degradation due to the breakdown of the polymer chains. This can lead to color changes, loss of elasticity, and reduced adhesion. UV-resistant or weather-resistant silicone sealants are formulated to withstand such exposure.
- Temperature Fluctuations:Extreme temperatures can cause silicone sealants to expand and contract, which might weaken their bonds and lead to cracking or detachment. Sealants with a wide temperature range (high and low) are preferable for applications in environments with temperature variations.
- Chemical Exposure:Contact with chemicals, solvents, oils, and other harsh substances can cause silicone sealants to break down or lose their adhesion properties. It’s important to select sealants that are compatible with the specific chemicals they might come into contact with.
- Moisture and Water:While silicone sealants are generally water-resistant, prolonged exposure to water or moisture can still lead to deterioration over time, especially if water manages to seep beneath the sealant. Waterproof silicone formulations are designed to offer enhanced resistance to water intrusion.
- Substrate Compatibility:The type of surfaces being sealed affects the longevity of the silicone sealant. Some substrates may be more prone to movement, expansion, or contraction, which can stress the sealant and potentially cause it to fail. It’s essential to choose a sealant that is compatible with the specific materials it will be adhered to.
- Joint Design and Preparation:Proper joint design and surface preparation play a significant role in the effectiveness of silicone sealants. Uneven surfaces, contaminants, or inadequate joint dimensions can hinder proper bonding and lead to premature failure.
- Application Technique:The way the sealant is applied can impact its performance. Over-application or under-application can affect adhesion and flexibility. Following the manufacturer’s recommended application guidelines is crucial for optimal results.
- Curing Time:Silicone sealants require time to fully cure and achieve their maximum performance. Premature exposure to stress or environmental factors before complete curing can compromise the sealant’s durability.
- Mechanical Stress:Silicone sealants can accommodate a certain degree of movement and stress, but excessive movement or stress beyond their designed limits can lead to cracking, detachment, or failure.
- Aging and Degradation:Over time, all materials, including silicone, undergo aging and degradation processes. Exposure to environmental factors can accelerate this process. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify signs of deterioration and prompt timely replacements.
To ensure the longevity and effectiveness of silicone sealants, it’s crucial to select the appropriate type of sealant for the specific application, follow proper installation and maintenance procedures, and consider the environmental conditions the sealant will be exposed to. Manufacturers often provide technical data and guidelines to help users choose the right sealant and ensure its proper application.
How Do Environmental Factors Influence the Longevity of Silicone Sealants?
The longevity of silicone sealants is influenced by various environmental factors that can affect their performance and durability over time. Silicone sealants are commonly used for their flexibility, adhesion, and resistance to weathering. However, exposure to different environmental conditions can impact their overall lifespan. Here are some key environmental factors that influence the longevity of silicone sealants:
- Temperature Fluctuations:Extreme temperatures can cause silicone sealants to expand and contract, leading to stress on the material and potential cracking or breaking of the sealant bond. Frequent and severe temperature fluctuations can accelerate degradation.
- UV Radiation:Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can cause the breakdown of the polymer chains in silicone sealants, leading to the loss of elasticity and adhesion properties. Over time, UV exposure can make the adhesive brittle and less effective.
- Moisture and Water:Silicone sealants are generally resistant to water, but prolonged exposure to water, moisture, or high humidity can lead to the growth of mold and mildew behind or within the sealant. This can weaken the sealant’s adhesion and compromise its integrity.
- Chemical Exposure:Contact with certain chemicals, solvents, oils, and cleaning agents can weaken the bond of silicone sealants and lead to degradation. It’s essential to choose adhesives resistant to the specific chemicals in the environment where they will be used.
- Air Pollution and Contaminants:Airborne pollutants, such as smog and industrial emissions, can contribute to the deterioration of silicone sealants over time. These pollutants can react with the sealant’s surface, causing discoloration, degradation, or loss of adhesion.
- Mechanical Stress:Physical stress caused by movements in the substrate, building settling, or vibrations can strain silicone sealants and potentially lead to cracking or detachment. Using flexible and elastic adhesives can help accommodate these movements.
- Substrate Compatibility:The material to which the silicone sealant is applied can also impact its longevity. The sealant must adhere well to the substrate, and differences in thermal expansion rates between the adhesive and the substrate can affect the sealant’s performance.
- Exposure to Environmental Elements:Environmental factors such as wind, rain, snow, and ice can stress more on silicone sealants. Sealants exposed to these elements should be formulated to withstand the specific conditions they will face.
To maximize the longevity of silicone sealants, it’s essential to choose high-quality adhesives designed for the specific environmental conditions they will be exposed to. Regular inspections and maintenance can also help identify early signs of degradation, allowing for timely replacement or repair of the sealants. Proper installation techniques, surface preparation, and substrate compatibility also play crucial roles in ensuring the durability of silicone sealants in various environments.
What Are Some Common Challenges Faced in Maintaining Silicone Sealant Integrity?
Maintaining the integrity of silicone sealants can be crucial for ensuring their effectiveness in various applications, such as sealing gaps, joints, and connections in construction, automotive, and other industries. Here are some common challenges faced in maintaining silicone sealant integrity:
- Adhesion Issues:Poor adhesion to substrates can lead to sealant failure. Proper surface preparation, including cleaning, drying, and sometimes using primers, is essential to ensure good adhesion.
- Substrate Compatibility:Silicone sealants may not adhere well to specific substrates, such as certain plastics or oily surfaces. Understanding the compatibility of the sealant with the substrate is crucial to avoid adhesion problems over time.
- UV Degradation:Exposure to sunlight and UV radiation can lead to the degradation of silicone sealants over time, causing them to become brittle, discolored, and less effective. Strategies to combat this challenge are UV-resistant formulations or protecting bonds from direct sunlight.
- Temperature Extremes:Extreme temperatures can cause silicone sealants to expand, contract, or become less flexible, compromising their integrity. Selecting adhesives designed for the expected temperature range is essential to prevent failure.
- Chemical Exposure:Silicone sealants might deteriorate when exposed to certain chemicals, solvents, or corrosive substances. Using chemically resistant adhesives or protecting them from harmful substances can mitigate this challenge.
- Movement and Flexibility:Sealants need to maintain flexibility without losing adhesion in applications with significant movement or vibration, such as in building joints or vehicle components. Inadequate flexibility can lead to cracking or detachment.
- Aging and Degradation:Over time, even without exposure to extreme conditions, silicone sealants can degrade due to natural aging processes. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify deteriorating adhesives before they cause problems.
- Improper Application:Incorrect application techniques, such as using too much or too little sealant, uneven application, or insufficient curing time, can lead to sealant failure. Following manufacturer guidelines for application is essential.
- Contamination:Dust, debris, moisture, or oily residues on the substrate or within the sealant can hinder proper adhesion and performance. Thorough cleaning and adequate application techniques can help prevent contamination-related issues.
- Inadequate Curing:Silicone sealants require sufficient time to cure and achieve their maximum properties. Rushing the curing process or exposing the adhesive to adverse conditions before it’s fully cured can compromise its integrity.
- Improper Joint Design:Inadequate joint design, such as insufficient depth or wrong dimensions, can affect the performance of silicone sealants. Standard design guidelines should be followed to ensure the sealant accommodates movement and stress.
- Improper Maintenance:Neglecting regular inspections and maintenance can lead to unnoticed deterioration of silicone sealants. Implementing a maintenance schedule and promptly addressing issues can extend the life of the adhesive.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of proper material selection, thorough preparation, skilled application, and ongoing maintenance. Manufacturers’ guidelines and industry best practices should be followed to maximize the integrity and longevity of silicone sealants in various applications.
How Does Cure Time Affect the Performance of Silicone Sealants?
The cure time of silicone sealants refers to the duration for the adhesive to fully set and achieve its desired properties. Cure time can significantly impact the performance of silicone sealants, influencing factors such as strength, adhesion, flexibility, and overall durability. Here’s how to cure time affects the performance of silicone sealants:

- Strength and Adhesion: Silicone sealants need time to cross-link and form a strong bond chemically. During the curing process, the adhesive goes through a chemical reaction, often involving the release of acetic acid or other byproducts. This reaction is essential for achieving proper adhesion and strength. If a silicone sealant is not allowed enough time to cure, it might not develop the necessary bond strength, leading to weaker adhesion and a higher risk of failure.
- Flexibility: Silicone sealants are known for their flexibility and ability to accommodate movement. The curing process contributes to the development of the sealant’s flexibility. Insufficient cure time can result in an adhesive that lacks the desired level of elasticity, causing it to crack or break when subjected to movement or thermal expansion and contraction.
- Water and Weather Resistance: Adequate cure time is crucial for developing a sealant’s resistance to water, weather, and environmental elements. A fully cured silicone sealant forms a barrier that prevents moisture and air infiltration. If the adhesive is not allowed to heal correctly, it might remain susceptible to water intrusion, reducing its effectiveness in sealing gaps or joints.
- Chemical Resistance: Silicone sealants are often used in environments where they might come into contact with chemicals or harsh substances. A proper cure is necessary to ensure the sealant can resist chemical degradation and maintain its integrity over time. Incomplete curing can lead to an adhesive more prone to chemical attack.
- Durability: The longevity of a silicone sealant is closely tied to its cure time. An adhesive that can cure fully tends to have a longer service life than one that hasn’t healed properly. Premature exposure to stress, movement, or environmental factors before curing is complete can compromise the durability of the sealant.
- Aesthetic Appearance: Cure time can also impact the visual appearance of the sealant. A sealant that has yet to cure completely might remain tacky or soft to the touch, attracting dust and debris and affecting its overall appearance.
To ensure optimal performance, following the manufacturer’s recommended cure time for the specific silicone sealant being used is essential. This time can vary based on the formulation of the adhesive, its intended application, and environmental conditions. Rushing the process by not allowing sufficient cure time can lead to subpar results and potentially costly failures down the line.
What Factors Can Impact the Durability of Silicone Sealants?
The durability of silicone sealants can be influenced by various factors, affecting their performance and longevity. Here are some key factors that can impact the durability of silicone sealants:
- Substrate Preparation:The surface where the silicone sealant will be applied needs to be clean, dry, and free of dust, dirt, oil, and other contaminants. Poor substrate preparation can hinder the adhesion of the sealant, leading to reduced durability.
- Adhesion:Proper adhesion is crucial for the longevity of the sealant. The compatibility of the silicone sealant with the substrate material is essential. Some adhesives are designed for specific substrates like glass, metal, or plastic, so using the appropriate type is necessary.
- Curing Time:Silicone sealants require sufficient curing time to reach their maximum strength and durability. Curing time can vary based on the specific product and environmental conditions. Applying stress or load on the sealant before it’s fully cured can compromise its performance.
- Temperature and Humidity:Environmental conditions during and after application can affect curing. Extreme temperatures or high humidity levels can alter the curing time and impact the final strength and durability of the sealant.
- UV Exposure:Silicone sealants exposed to direct sunlight and UV radiation can experience degradation and reduced flexibility over time. UV-resistant or UV-stable bonds are available for applications where exposure to sunlight is a concern.
- Chemical Exposure:Exposure to harsh chemicals or solvents can weaken the silicone sealant’s structure, reducing durability. Using chemically resistant adhesives in areas with potential exposure to such substances is advisable.
- Movement and Stress:Silicone sealants are often used in joints that experience movement due to building settling, thermal expansion, or vibration. Excessive exercise can prevent the adhesive from failing over time if properly accounted for.
- Joint Design:Proper joint design, including appropriate width-to-depth ratios, can impact the sealant’s ability to accommodate movement and stress without failing. More collaborative design is needed to avoid premature failure.
- Quality of Sealant:The quality of the silicone sealant, including its formulation and manufacturer, plays a significant role in its durability. Using reputable brands and products can improve the chances of achieving a long-lasting seal.
- Maintenance:Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify and address any issues with the sealant before they become significant problems. This proactive approach can extend the lifespan of the adhesive.
- Application Technique:Applying the sealant correctly, including ensuring uniform thickness and proper sealant tooling, can contribute to its long-term performance.
It’s essential to consider these factors when selecting, applying, and maintaining silicone sealants in various applications, such as construction, automotive, or household use, to ensure they provide the expected level of durability and performance.
How Do Environmental Factors Influence the Longevity of Silicone Sealants?
The longevity of silicone sealants can be influenced by various environmental factors that affect their physical and chemical properties over time. Silicone sealants are commonly used for their flexibility, durability, and resistance to moisture and temperature extremes. However, even these resilient materials can degrade over time due to exposure to specific environmental conditions. Here are some of the critical environmental factors that can influence the longevity of silicone sealants:
- Temperature Extremes: Silicone sealants are known to withstand a wide range of temperatures, but extreme heat or cold can still impact their performance. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause the silicone to become brittle and lose flexibility, making it more prone to cracking and breaking. Similarly, extreme cold can cause the silicone to become less flexible, reducing its ability to accommodate movement without tearing or failing.
- UV Radiation: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can lead to the degradation of silicone sealants. UV radiation can break down the chemical bonds in the silicone polymer, leading to a loss of elasticity, color fading, and overall deterioration of the sealant’s physical properties. To combat this, some silicone sealants are formulated with UV-resistant additives.
- Moisture and Water: Silicone sealants are generally resistant to moisture and water, but prolonged exposure to water or constant immersion can break the sealant’s structure. Water infiltration can weaken the adhesion between the adhesive and the substrate, causing leaks and compromising the seal’s effectiveness.
- Chemical Exposure: Contact with certain chemicals, solvents, or cleaning agents can cause silicone sealants to swell, shrink, or lose their adhesive properties. Chemical exposure can break down the molecular structure of silicone, resulting in reduced durability and performance.
- Mechanical Stress and Movement: Silicone sealants are commonly used to provide a flexible barrier between materials that might experience movement or vibration. Continuous exercise or stress on the adhesive can lead to fatigue and eventual failure, as the glue might not be able to maintain its integrity over time.
- Air Pollution and Contaminants: Airborne pollutants, such as smog and industrial emissions, can settle on the surface of silicone sealants. Over time, these pollutants can react with silicone and contribute to its degradation. This can be especially pronounced in urban or industrial areas.
- Humidity and Humid Environments: While silicone sealants are generally resistant to moisture, high humidity levels or exposure to a consistently humid environment can impact their performance. Prolonged exposure to high humidity can lead to mold growth or reduce the sealant’s adhesive strength.
To ensure the longevity of silicone sealants, it’s essential to choose the right type of sealant for the specific application and environment. Additionally, proper installation techniques, regular maintenance, and periodic inspections can help identify any potential issues before they lead to failure. Using sealants specifically designed for outdoor or high-UV environments, and following the manufacturer’s guidelines for application and maintenance, can help extend the lifespan of silicone sealants.
What Are Some Common Challenges Faced in Maintaining Silicone Sealant Integrity?
Maintaining silicone sealant integrity ensures its effectiveness in various applications such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. However, several common challenges can arise during the process of maintaining silicone sealant integrity:
- Adhesion Issues: Silicone sealants may need help to adhere correctly to specific substrates, especially if the surface is not adequately cleaned, prepared, or primed. Poor adhesion can lead to leaks and reduced sealing effectiveness.
- Surface Preparation: Inadequate cleaning and preparation of the characters to be sealed can lead to poor adhesion. Any contaminants, oils, dust, or previous sealant residue should be removed to ensure proper bonding.
- Compatibility: Not all silicone sealants are compatible with every type of material. Different formulations of adhesives are designed for specific substrates (e.g., glass, metal, plastics). Using the wrong type of silicone sealant can result in poor adhesion, reduced longevity, and potential damage to the material.
- UV and Weather Exposure: Outdoor applications are subjected to various environmental conditions, including sunlight, rain, and temperature fluctuations. Over time, exposure to UV radiation and harsh weather can cause silicone sealants to degrade, become discolored, and lose elasticity.
- Temperature Extremes: Extreme hot and cold temperatures can impact silicone sealants’ flexibility and adhesion. In freezing temperatures, the adhesive can become brittle and crack, while excessive heat can cause it to soften and lose its integrity.
- Chemical Exposure: Silicone sealants may be exposed to chemicals, solvents, or cleaning agents that can degrade their composition, resulting in reduced effectiveness and compromised sealing properties.
- Joint Movement: In applications with joint movement due to expansion, contraction, or vibrations, the silicone sealant needs to be flexible enough to accommodate these movements without losing its bond or developing cracks.
- Aging and Degradation: Over time, even without exposure to extreme conditions, silicone sealants can naturally age and deteriorate, leading to reduced flexibility, adhesion, and overall performance.
- Improper Application Technique: Misapplying silicone sealant can result in uneven coverage, air pockets, or improper sealing. This can compromise the integrity of the seal and lead to leaks.
- Curing Time: Silicone sealants require a specific time to cure properly. Rushing the process can lead to premature exposure to external factors and compromise the integrity of the adhesive.
- Joint Design: Poor joint design, such as improper dimensions or inadequate expansion space, can put undue stress on the silicone sealant and lead to failure over time.
- Sealant Quality: Low-quality or expired silicone sealants can result in subpar performance and reduced integrity. It’s important to use reputable brands and ensure the adhesive is within its recommended shelf life.
To address these challenges, it’s essential to follow proper installation guidelines, choose the type of silicone sealant for the specific application, and take appropriate measures to prepare surfaces and ensure adequate curing. Regular inspection and maintenance can also help identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
What Innovations Are Driving the Evolution of Silicone Sealants?
Numerous innovations steer the evolution of silicone sealants. Initially, silicone sealants were simple, offering essential adhesion and flexibility. Nevertheless, recent advancements in chemistry and materials have led to remarkable improvements.
Novel formulations have enhanced sealants’ resistance to extreme high and low temperatures. This progress is crucial in applications where conventional adhesives, such as aerospace and industrial settings, would fail.
The longevity of silicone sealants has also seen progress due to improved crosslinking techniques. This ensures a more durable and long-lasting bond, reducing the need for frequent reapplications.
In sustainability, there have been strides in developing eco-friendly silicone sealants. These formulations have reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and incorporate more sustainable raw materials.
Furthermore, self-healing silicone sealants have emerged, allowing minor cracks to mend autonomously. This is a game-changer for maintenance, particularly in structures that are hard to access.
The incorporation of nanoparticles has resulted in sealants with heightened mechanical properties. These nanocomposite sealants exhibit superior strength and can withstand more significant stresses.
Additionally, improved dispensing systems and application methods have streamlined the use of silicone sealants, making them more convenient and efficient for various projects.
How is Research Expanding the Range of Applications for Silicone Sealants?
Research is broadening the scope of applications for silicone sealants in various ways. By exploring innovative formulations and engineering techniques, silicone sealants are being adapted for increasingly diverse uses.
In construction, silicone sealants are finding new roles beyond traditional sealing and bonding. Studies are uncovering ways to enhance their resistance to harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for sealing joints in high-rise buildings and bridges. Moreover, ongoing research is improving the fire-retardant properties of silicone sealants, expanding their utility in fireproofing applications.
The automotive sector is another area benefitting from advanced research. Silicone sealants are being investigated for their potential to replace traditional gaskets, offering better longevity and performance. Researchers are optimizing the composition of these sealants to ensure compatibility with various automotive fluids and to withstand the stresses of engine operation.
In healthcare, silicone sealants are examined for their biocompatibility and medical-grade applications. Ongoing studies aim to develop sealants that can safely interact with human tissues, thus opening doors for wound closure and surgical procedures. This potential is driving the exploration of novel formulations and sterilization methods.
The electronics industry is also experiencing an impact from silicone sealant research. As electronic devices become more compact and intricate, the need for adequate moisture and thermal protection is growing. Researchers are refining silicone sealants to offer superior moisture resistance and thermal conductivity, crucial for safeguarding delicate electronic components.
Furthermore, sustainability is a critical consideration in current research endeavors. Efforts are being directed towards creating eco-friendly silicone sealants by incorporating bio-based materials or improving their recyclability. This aligns with the global push for greener technologies and reduced environmental impact.
To summarize, ongoing research is expanding the potential applications of silicone sealants across multiple industries. These sealants are becoming indispensable in the construction, automotive, healthcare, electronics, and sustainable technology sectors through formulation advancements and innovative approaches. The outcomes of this research promise to reshape how we utilize silicone sealants in the future.
Where Do Experts See the Future of Silicone Sealant Development Heading?
However, please note that developments in this field might have occurred since then.
- Advanced Formulations:Experts may anticipate the development of silicone sealants with enhanced properties, such as improved flexibility, adhesion, and durability. Researchers might develop adhesives that withstand extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and other environmental stresses.
- Environmentally Friendly Options:Given the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental concerns, the future of silicone sealant development could involve the creation of more eco-friendly formulations. This might include reducing or eliminating volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful chemicals and exploring bio-based or renewable materials.
- Innovative Sealants:With the advancement of intelligent materials and the Internet of Things (IoT), silicone sealants could be developed to have sensing capabilities. These “smart” sealants might change color or texture when exposed to certain conditions, providing visual indications of leaks or structural changes.
- Self-Healing Properties:Developing self-healing silicone sealants could revolutionize their use in various applications. These sealants can repair tiny cracks or damage autonomously, extending their lifespan and improving their effectiveness.
- Nanotechnology Integration:Nanomaterials could play a role in the future of silicone sealants by enhancing their mechanical properties, adhesion, and resistance to environmental factors. Nanoparticles could be incorporated to create more robust and more durable bonds.
- Customization and Specialty Applications:Silicone sealant development might focus on creating formulations tailored to specific industries or applications. Sealants designed for automotive, aerospace, construction, or electronics might have unique requirements that drive specialized development efforts.
- Faster Curing and Application Techniques:Advancements in curing technologies, such as UV curing or rapid moisture-curing systems, could make silicone sealants more convenient to use. Shorter curing times could lead to increased productivity in various industries.
- Enhanced Adhesion to Diverse Surfaces:Future developments might focus on improving the ability of silicone sealants to adhere to a wide range of substrates, including challenging surfaces like plastics, composites, and low-energy materials.
- Regulatory Compliance:As regulations and standards related to safety and environmental impact evolve, silicone sealant development may need to align with these changes. This could involve creating sealants that meet stricter health, safety, and sustainability guidelines.
- Collaboration with Other Industries:Interdisciplinary collaboration might play a role in shaping the future of silicone sealants. For instance, cross-industry partnerships could include advancements in chemistry, material science, and engineering.
What is the Environmental Impact of Silicone Sealants?
The environmental impact of silicone sealants can vary based on factors such as their composition, manufacturing processes, usage patterns, and end-of-life considerations. Here are some key points to consider:
- Raw Materials and Manufacturing:Silicone sealants are typically made from silicone polymers derived from silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The production of silicone polymers involves energy-intensive processes, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The raw materials used in silicone production are often derived from fossil fuels, which can have environmental implications.
- VOC Emissions:Traditional silicone sealants can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during curing and as they age. VOCs contribute to indoor and outdoor air pollution, adversely affecting air quality and human health.
- Durability and Longevity:Silicone sealants are known for their durability and resistance to environmental stresses. This can be beneficial from an ecological standpoint because longer-lasting adhesives require less frequent replacement, thus reducing waste.
- End-of-Life Considerations:When silicone sealants reach the end of their lifespan and need to be removed or replaced, there can be disposal-related challenges. Silicone waste can be difficult to recycle due to its chemical composition and the potential for contamination. Improper disposal could lead to accumulation in landfills.
- Biodegradability and Recycling:Conventional silicone sealants are not biodegradable, and recycling options for silicone products are limited. However, researchers are exploring ways to develop more environmentally friendly silicone materials that can degrade over time or be recycled.
- Eco-Friendly Formulations:Responding to environmental concerns, some manufacturers are developing silicone sealants with reduced VOC content, lower environmental impact, and improved sustainability profiles. These formulations may use bio-based or renewable materials to mitigate the adverse effects of traditional silicone sealants.
- Energy Efficiency and Insulation:Silicone sealants are used in construction and other industries to provide insulation and improve energy efficiency. While this can have positive environmental implications by reducing energy consumption, it’s essential to consider the overall lifecycle impact of the sealants.
- Regulatory Compliance:Environmental regulations and standards vary by region. Manufacturers of silicone sealants may need to adhere to specific guidelines to mitigate their environmental impact and ensure their products are safe.
Overall, the environmental impact of silicone sealants involves a complex interplay of factors. As environmental awareness increases, the industry is likely to continue exploring ways to develop more sustainable formulations, improve recycling and disposal options, and reduce the overall footprint of silicone sealants throughout their lifecycle.
How Are Manufacturers Working to Develop More Environmentally Friendly Silicone Sealant Formulations?
Manufacturers of silicone sealants are actively working to develop more environmentally friendly formulations due to increasing concerns about sustainability and environmental impact. Several strategies and approaches are being employed to achieve this goal:
- Raw Material Selection:Manufacturers choose raw materials with a lower environmental impact. This includes using bio-based or renewable feedstocks and selecting components with lower energy consumption during production.
- Reduced Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):VOCs in sealants can contribute to air pollution and have adverse health effects. Manufacturers are formulating silicone sealants with lower VOC content or creating VOC-free options to minimize emissions.
- Solvent-Free Formulations:Traditional silicone sealants often contain solvents that can harm the environment and human health. Manufacturers are developing solvent-free or low-solvent formulations to reduce the release of harmful substances during application and curing.
- Recycled Materials:Some manufacturers are incorporating recycled materials into their silicone sealant formulations, reducing the demand for virgin resources and promoting circular economy practices.
- Energy-Efficient Production Processes:Manufacturers optimize their production processes to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing. This might involve using more energy-efficient equipment or adopting innovative production techniques.
- Longevity and Durability:Silicone sealants are designed to create long-lasting seals, reducing the need for frequent reapplications and thereby minimizing waste. Manufacturers are focusing on creating adhesives with enhanced durability and weather resistance.
- Biodegradability:Research is being conducted into developing silicone sealants that can biodegrade over time, reducing their impact on the environment after their useful life.
- Water-Based Formulations:Water-based silicone sealants are being developed as an alternative to solvent-based products. Water-based formulations generally have lower environmental impact and fewer health risks.
- Life Cycle Analysis:Manufacturers are conducting life cycle assessments to understand the overall environmental impact of their products, from raw material extraction to disposal, and using these insights to guide formulation improvements.
- Certifications and Standards:Manufacturers are pursuing certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and Green Seal, which indicate that their products meet specific environmental performance criteria.
- Collaboration and Research:Industry collaborations, partnerships with research institutions, and engagement with environmental organizations help manufacturers access the latest research and innovative ideas for developing more sustainable silicone sealants.
- Consumer Education:Manufacturers are working to educate consumers about the benefits of environmentally friendly silicone sealants, encouraging them to choose products that align with their sustainability goals.
In summary, manufacturers of silicone sealants are employing a combination of raw material selection, formulation changes, production process improvements, and collaboration to develop more environmentally friendly products that meet the demands of both consumers and environmental regulations.