Hot Melt Adhesive

Hot melt adhesive is a versatile and efficient bonding solution that has gained prominence across various industries due to its unique properties and wide-ranging applications. This adhesive formulation, known as hot glue, is heated to a molten state before being applied, allowing it to create strong bonds as it cools and solidifies. Its ability to adhere to many materials, along with its rapid setting time and durability, has made it a preferred choice for tasks ranging from product assembly and packaging to woodworking and textiles.
In exploring hot melt adhesive, we delve into its composition, working mechanisms, applications, and benefits, shedding light on how it enhances modern production processes.
What is Hot Melt Adhesive, and How Does It Differ from Other Adhesives?
Hot melt adhesive, or hot glue, is a thermoplastic adhesive applied in a molten state and then cools and solidifies to form a bond. It is widely used in various industries and applications due to its fast bonding capabilities, versatility, and ease of use. Hot melt adhesives are typically supplied in solid stick or pellet forms that are melted using specialized hot glue guns, dispensers, or melting equipment. The molten adhesive is then applied to the surfaces to be bonded, and as it cools and solidifies, it forms a strong bond.
Here are some key characteristics and differences between hot melt adhesives and other types of bonds:
- Application Temperature:
- Hot Melt Adhesives: These adhesives are molten at elevated temperatures, usually between 250 and 400°F (121 to 204°C).
- Other Adhesives: Conventional adhesives like water-based, solvent-based, or reactive adhesives may require lower or higher application temperatures, depending on their chemistry.
- Setting Time:
- Hot Melt Adhesives: They cool and solidify quickly, usually within seconds to minutes, creating an almost instant bond.
- Other Adhesives: The setting time for other adhesives can vary widely, from seconds to hours or even longer, depending on the type and application.
- Chemistry:
- Hot Melt Adhesives: These adhesives are made from thermoplastic polymers that soften and melt upon heating and solidify upon cooling. They don’t involve chemical reactions for bonding.
- Other Adhesives: Other adhesive types, like epoxy, polyurethane, and cyanoacrylate (super glue), typically form bonds through chemical reactions that cure and harden the adhesive.
- Bond Strength and Flexibility:
- Hot Melt Adhesives: They generally provide good initial bond strength. However, their long-term durability and resistance to extreme conditions (such as high heat or exposure to solvents) might be lower than other adhesive types.
- Other Adhesives: Certain adhesives, such as epoxy or polyurethane, can offer higher bond strength and better resistance to harsh environments.
- Versatility and Ease of Use:
- Hot Melt Adhesives: They are versatile and easy to use since they don’t require mixing or complicated application procedures. They are often used for packaging, crafts, and non-structural bonding applications.
- Other Adhesives: Some other adhesives might require more precise application techniques, curing times, or specific environmental conditions.
- Applications:
- Hot Melt Adhesives: They are used in packaging, woodworking, product assembly, textiles, and crafts.
- Other Adhesives: Different adhesives are favored in various industries, such as epoxy for construction and automotive, cyanoacrylate for electronics, and polyurethane for flexible substrates.
How is Hot Melt Adhesive Formulated and Manufactured?
Hot Melt Adhesive (HMA), also known as hot glue, is a thermoplastic adhesive applied in a molten state and solidifies as it cools, creating a solid bond. The formulation and manufacturing process of hot melt adhesive involves several steps. Here’s a general overview of the process:
Formulation:
- Selecting Base Polymers:The first step is to choose the base polymers that will form the bulk of the adhesive. Common polymers include ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), polyethylene, polypropylene, and styrene-block copolymers.
- Adding Resins:Resins are added to improve tackiness, adhesion, and flexibility. These can include tackifying rosin derivatives, hydrocarbon resins, and terpene resins.
- Incorporating Fillers:Calcium carbonate, silica, or talc may be added to adjust the adhesive’s viscosity, improve its thermal stability, and control cost.
- Incorporating Additives:Antioxidants, UV stabilizers, and colorants are introduced to enhance the adhesive’s performance and appearance.
- Mixing and Melting:The selected polymers, resins, fillers, and additives are mixed using specialized equipment. The mixture is then melted at controlled temperatures to create a homogenous molten adhesive.
Manufacturing:
- Extrusion and Compounding:The molten adhesive mixture is extruded through a die to create a continuous ribbon or bead of adhesive. The bond is typically maintained at a consistent temperature to ensure proper viscosity during this process.
- Cooling and Solidification:The hot glue is cooled rapidly using either air-cooling or water-cooled rollers after extrusion. This solidifies the adhesive into its final form.
- Cutting and Packaging:Once the adhesive has hardened, it is cut into the desired shapes, such as sticks, pellets, or blocks. These forms are then packaged in suitable containers for distribution, such as bags or boxes.
- Quality Control:Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure the adhesive’s consistency, adhesive properties, and other performance characteristics meet the specified standards.
- Application:End-users, such as industrial manufacturers or consumers, apply the hot melt adhesive using hot glue guns or other specialized equipment. The adhesive is heated to a molten state and applied to the substrate. As it cools and solidifies, it forms a strong bond.
What Are the Key Components of Hot Melt Adhesive?
Hot melt adhesives, also known as hot glue, are thermoplastic materials applied in a molten state and solidify upon cooling to form a strong bond. The critical components of hot melt adhesives typically include:
- Polymers:The main component of hot melt adhesives is a polymer, which is a long-chain molecule. Different types of polymers are used to achieve specific adhesive properties. Common polymer types include ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), polyethylene, polypropylene, polyamide (nylon), and styrene block copolymers (such as SBS and SIS).
- Resins:Resins are often added to improve the adhesive’s properties, such as flexibility, tackiness, and adhesion to different surfaces. These resins can be natural or synthetic and significantly determine the adhesive’s overall performance.
- Fillers:Fillers are added to hot melt adhesives to modify their characteristics and improve properties like viscosity, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness. Joint fillers include calcium carbonate, talc, silica, and glass beads.
- Tackifiers:Tackifiers enhance the adhesive’s tackiness, which refers to its ability to bond to surfaces upon contact quickly. Tackifiers are often aromatic resins that increase the initial grab and stickiness of the adhesive.
- Plasticizers:Plasticizers are added to improve the flexibility and elongation of the adhesive. They help maintain the adhesive’s bond under various conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and movement.
- Antioxidants and Stabilizers:These additives are used to prevent the degradation of the adhesive due to exposure to heat, light, and oxygen. They help prolong the adhesive’s shelf life and maintain its performance over time.
- Colorants:Colorants are added to provide the adhesive with a specific color. This can be important for applications where aesthetics are a concern, such as in the packaging industry.
- Waxes:Waxes are sometimes added to hot melt adhesives to modify their rheological properties (flow behavior) and improve their processing characteristics.
- Modifiers:Various modifiers can be added to hot melt adhesives to tailor their properties for specific applications. These may include flame retardants, UV stabilizers, and other specialized additives.
How Does Hot Melt Adhesive Achieve Bonding?
Hot melt adhesives achieve bonding through a simple and effective process that involves a few key steps:
- Heating and Melting:Hot melt adhesives start as solid pellets or blocks at room temperature. They are heated in specialized hot melt adhesive application equipment, such as a hot glue gun or a hot melt adhesive dispenser. The heat causes the adhesive to melt and become a viscous liquid.
- Application:Once the adhesive is molten, it can be applied to the surfaces that need to be bonded. This is typically done by extruding the molten adhesive through a nozzle or applicator onto one or both bonded substrates.
- Contact and Compression:The adhesive is applied directly onto the surfaces that are to be bonded. The substrates are then brought together while the adhesive is still molten. This step is essential because it ensures good contact between the adhesive and the surfaces, maximizing its ability to form strong bonds.
- Cooling and Solidification:As the molten adhesive comes into contact with the more excellent surfaces of the substrates, it begins to cool and solidify rapidly. The solidification process occurs relatively quickly, often within seconds to minutes, depending on factors like adhesive composition, substrate materials, and environmental conditions.
- Bond Formation:During solidification, the adhesive undergoes a phase change from liquid to solid. As it solidifies, the adhesive molecules interlock with the molecules of the substrate surfaces. This creates mechanical stable bonds and adhesion between the adhesive and the substrates.
- Curing:While hot melt adhesives do not require a curing process like some other adhesives, they continue to develop strength over time as they cool and harden. However, they achieve their initial bond strength almost immediately after solidification.
What Are the Advantages of Using Hot Melt Adhesive?
Hot melt adhesives offer a range of advantages that make them popular for various applications across industries. Some of the key benefits of using hot melt adhesive include:
- Fast Bonding:Hot melt adhesives solidify quickly upon cooling, allowing for rapid assembly and production processes. This speed can lead to increased productivity and efficiency in manufacturing operations.
- Versatility:Hot melt adhesives can bond with various substrates, including plastics, wood, metal, paper, fabric, and more. This versatility makes them suitable for diverse packaging, automotive, electronics, woodworking, and textile applications.

- No Solvents or Water:Hot melt adhesives are solvent-free and water-based, which means they do not contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or require water for application. This can contribute to a safer and more environmentally friendly workplace.
- Ease of Use:Hot melt adhesives are easy to handle and apply. They are typically supplied as solid pellets or blocks that can be melted using specialized equipment such as hot glue guns or dispensers. The absence of complex mixing or curing processes simplifies the bonding procedure.
- Clean Application:Hot melt adhesives are applied in a molten state, which allows for precise application and clean bonds without dripping or mess. This cleanliness is particularly advantageous for applications where aesthetics and cleanliness are essential.
- Strong Bonds:Hot melt adhesives create strong bonds quickly after solidification. They exhibit good adhesion and cohesive strength, making them suitable for applications where mechanical stress and vibration resistance are essential.
- Minimal Wastage:Since hot melt adhesives solidify rapidly, there is minimal time for adhesive wastage due to evaporation or excessive spreading. This efficiency can lead to cost savings over time.
- Wide Temperature Range:Hot melt adhesives can withstand a range of temperatures, from low to high, depending on the specific formulation. This adaptability is valuable for applications that experience varying environmental conditions.
- Good Gap-Filling Ability:Hot melt adhesives can fill gaps between substrates, improving bonding in uneven or irregular surfaces. This characteristic is helpful for applications where precise alignment may be challenging.
- Reduced Equipment Maintenance:Hot melt adhesive application equipment is relatively simple and requires less maintenance than other methods. This can lead to reduced downtime and lower maintenance costs.
- Reversible Bonds:Hot melt adhesives can offer reversibility in specific applications, allowing components to be easily separated without causing significant damage.
- Broad Industry Applications:Hot melt adhesives are used in packaging, automotive, textiles, woodworking, electronics, medical devices, and more, demonstrating their adaptability to various industries.
While hot melt adhesives have numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of each application and the potential limitations of these adhesives, such as their susceptibility to high temperatures or specific chemical exposures.
How Does Hot Melt Adhesive Compare to Solvent-Based Adhesives?
Hot melt and solvent-based adhesives are two different types of adhesives with distinct characteristics and advantages. Here’s a comparison of the two:
- Composition:
- Hot Melt Adhesives:Hot melt adhesives are solid at room temperature and become molten when heated. They comprise polymers, resins, and other additives that melt to form a bond upon cooling.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:Solvent-based adhesives are a polymer dissolved in a solvent carrier. The solvent evaporates during the bonding process, leaving a solid adhesive layer behind.
- Application Process:
- Hot Melt Adhesives:They are applied in a molten state using specialized equipment such as hot glue guns or dispensers. The adhesive solidifies quickly upon cooling, achieving rapid bonding.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:These adhesives are applied in liquid form. The solvent carrier allows the adhesive to flow and spread before evaporating, after which the adhesive cures and forms a bond.
- Drying Time:
- Hot Melt Adhesivessolidify quickly upon cooling, resulting in rapid bond formation within seconds to minutes.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:The drying and curing time can be longer due to the need for solvent evaporation and polymer cross-linking.
- VOC Emissions:
- Hot Melt Adhesives:They are generally considered to have low or no VOC emissions since they do not involve solvents.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:These adhesives may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application due to solvent evaporation. VOC emissions can contribute to environmental and health concerns.
- Strength and Durability:
- Hot Melt Adhesives:They provide strong initial bonds, but their long-term durability and resistance to extreme conditions might vary depending on the formulation.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:These adhesives can offer strong and durable bonds, particularly after the solvent evaporates and the adhesive is fully cured.
- Substrate Compatibility:
- Hot Melt Adhesives:They can bond with many substrates, including plastics, wood, and paper, although substrate compatibility can vary with the adhesive formulation.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:They can provide strong bonds on various substrates due to their ability to wet and penetrate surfaces.
- Environmental and Safety Considerations:
- Hot Melt Adhesives:They are generally considered safer for the environment and human health due to their lack of solvents and low VOC emissions.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:Solvent-based adhesives can pose environmental and health risks due to the emission of volatile organic compounds. Proper ventilation is often necessary during application.
- Shelf Life and Storage:
- Hot Melt Adhesivestypically have a longer shelf life and do not undergo curing or degradation during storage.
- Solvent-Based Adhesives:They might have a limited shelf life, and the solvent can evaporate over time, potentially affecting the adhesive’s performance.
Both hot melt adhesives and solvent-based adhesives have their strengths and weaknesses. The choice between the two depends on the specific application, performance requirements, environmental considerations, and ease of use. It’s important to carefully evaluate these factors to determine which adhesive type best suits your needs.
What Are the Various Forms of Hot Melt Adhesive Available?
Hot melt adhesives are thermoplastic materials applied in a molten state and solidify upon cooling to create a strong bond. They are commonly used in various industries due to their quick setting time, muscular bond strength, and versatility. Several forms of hot melt adhesive are available, each tailored to specific applications. Here are some of the common forms:
- Hot Melt Sticks or Glue Sticksare one of the most familiar forms of hot melt adhesive. They are cylindrical sticks of solid adhesive loaded into a hot glue gun. The gun heats the stick, melts the adhesive, and applies it to the substrate. Glue sticks are used for various applications, including crafts, woodworking, packaging, and more.
- Hot Melt Pellets or Granules:These are small, bead-like granules or pellets of hot melt adhesive that can be melted using specialized equipment. They are used in industrial applications, including packaging, bookbinding, textiles, automotive, electronics, and more. Pellets are versatile and can be melted and applied using various adhesive dispensing systems.
- Hot Melt Blocks or Slugs:Like pellets, hot melt blocks or slugs are a more significant adhesive material. They are often used in high-volume production lines requiring continuous adhesive supply. These blocks are loaded into larger hot melt applicators that can accommodate their size.
- Hot Melt Films or Sheets:Hot melt adhesive films are thin sheets of adhesive with a release liner on one or both sides. They are often used in textiles, apparel, footwear, and electronics industries. These films can be applied heat and pressure, making them suitable for bonding fabrics, foils, and other materials.
- Hot Melt Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives (HMPSA):Hot melt adhesives remain tacky even after solidifying. They are often used in applications requiring an adhesive bond, repositioning ability, and easy application, such as labels, tapes, and decals.
- Hot Melt Spray Adhesives:These adhesives are applied in a spray form, making them suitable for larger surfaces and irregular shapes. They are used in woodworking, furniture manufacturing, and automotive industries.
- Hot Melt Powders:These are fine powders that can be melted and applied as a molten adhesive. They are used in applications where the controlled application is essential, such as textiles and specific industrial processes.
- Hot Melt Strings or Ropes:These are thicker forms of hot melt adhesive that resemble strings or ropes. They are often used in sealing applications, such as carton sealing, case sealing, and packaging.
The choice of hot melt adhesive form depends on the application, the bonded materials, the required bond strength, production volume, and the available equipment. Selecting the appropriate form of hot melt adhesive is essential to ensure adequate bonding and desired performance in your specific application.
How Do Temperature and Pressure Affect Hot Melt Adhesive Bonding?
Temperature and pressure are two critical factors that significantly affect the bonding performance of hot melt adhesives. Proper control and management of these variables are essential to achieve solid and reliable adhesive bonds. Here’s how temperature and pressure impact hot melt adhesive bonding:
Temperature:
- Melting and Viscosity:Hot melt adhesives are solid at room temperature but become molten and fluid when heated. The adhesive’s melting point and viscosity determine how easily it flows and wets the substrate surfaces. The adhesive must be heated to an appropriate temperature to achieve the desired consistency for adequate bonding.
- Activation:Heating the adhesive to its optimal temperature range activates its adhesive properties, allowing it to penetrate the substrate’s microstructures and create a strong bond upon cooling and solidification.
- Open Time:Open time refers to the period during which the adhesive remains fluid and workable after application. The temperature affects the available time; higher temperatures can reduce the open time, requiring a faster application, while lower temperatures provide a longer open time.
- Solidification:Cooling the adhesive after application causes it to solidify and form a bond. Proper cooling ensures the adhesive sets properly and creates a strong bond with the substrate.
Pressure:
- Contact and Wetting:Applying pressure during adhesive application ensures an intimate connection between the adhesive and substrate surfaces. This facilitates proper wetting of the substrate and the penetration of the adhesive into microstructures, enhancing bond strength.
- Excess Adhesive Removal:Excessive pressure can squeeze out excess adhesive, leading to uneven bond lines, adhesive waste, and reduced strength. Finding the right balance between sufficient stress for good contact and too much pressure results in adhesive squeeze-out.
- Reducing Voids and Entrapped Air:Pressure helps minimize the presence of voids or air pockets between the adhesive and substrate. Proper pressure application helps ensure the adhesive fills gaps and irregularities in the substrate surface, leading to a more uniform and reliable bond.
- Setting and Curing:Pressure aids in holding the substrate surfaces together during the adhesive’s cooling and solidification process. This is particularly important for achieving strong initial bonds in applications requiring immediate bond strength.
- Enhancing Bond Strength:Adequate pressure applied during bonding contributes to improved mechanical interlocking between the adhesive and substrate, resulting in higher bond strength.
It’s important to note that the optimal temperature and pressure settings can vary based on the specific adhesive formulation, substrate materials, application method, and equipment used. Manufacturers often provide guidelines and recommendations for temperature and pressure settings to achieve optimal bonding results with their hot melt adhesive products. Proper experimentation and testing are crucial to finding the right combination of temperature and pressure for your specific bonding application.
What Are the Common Applications of Hot Melt Adhesive in Packaging?
Hot melt adhesives are widely used in packaging due to their versatility, efficiency, and fast-setting properties. They provide strong bonds, even in challenging packaging scenarios. Here are some typical applications of hot melt adhesive in packaging:
- Carton Sealing:Hot melt adhesives are often used to seal cartons, boxes, and cases. They create a strong bond that resists tampering and ensures the contents are secure during transit.
- Case and Tray Erecting:Hot melt adhesives are used in automated packaging lines to assemble cases, trays, and other containers. The fast-setting nature of hot melts speeds up production.
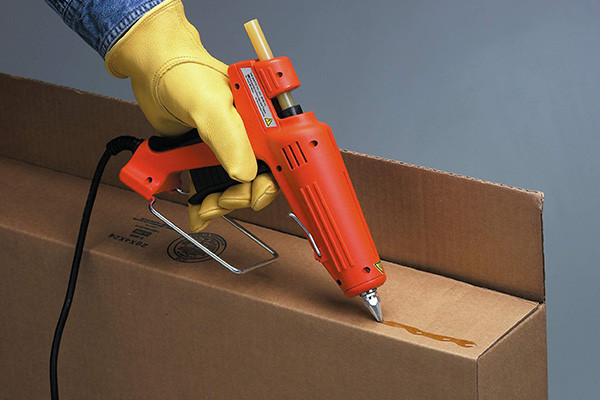

3.Labeling and Tagging:Hot melt adhesives attach labels, tags, and promotional materials to packaging. They provide a reliable bond that withstands various environmental conditions.
4.End-of-line Packaging:In end-of-line packaging applications, hot melt adhesives are used for sealing packages ready for distribution. This includes everything from individual products to larger palletized loads.
5.Bonding Display Units:Hot melt adhesives are used to create temporary or semi-permanent displays, often seen in retail environments. These displays can hold products and promotional materials.
6.Flexible Packaging:Hot melt adhesives create seals in flexible packaging, such as pouches, bags, and sachets. They offer strong bonds while allowing for flexibility in the packaging material.
7.Window Patching:In packaging designs with a window to display the product, hot melt adhesives attach the clear plastic window to the package.
8.Packaging Inserts:Hot melt adhesives attach inserts to packaging, such as product information cards or product samples. This ensures that the inserts stay securely in place.
9.Tamper-Evident Seals:Hot melt adhesives can create tamper-evident seals on the packaging, ensuring that consumers can easily detect if a package has been opened or tampered with.
10.Food Packaging:FDA-approved Hot melt adhesives can be used in food packaging applications. They often seal food containers, such as cartons or trays.
11.Bundling and Strapping:Hot melt adhesives are used to bundle products together, like cans or bottles, creating a secure grouping for distribution.
12.Bookbinding:In packaging printed materials, such as books and magazines, hot melt adhesives are used in the binding process to create durable and secure book spines.
13.Diaper and Hygiene Product Manufacturing:Hot melt adhesives are commonly used to bond various layers and components in diaper and hygiene product manufacturing.
The key advantages of hot melt adhesives in packaging include the following:
- Their fast-setting nature.
- Ease of application in automated processes.
- Strong bonds on various substrates.
- Versatility in different packaging scenarios.
However, it’s essential to choose the appropriate type of hot melt adhesive based on the packaging materials, environmental conditions, and specific requirements of the application.
How Is Hot Melt Adhesive Used in the Automotive Industry?
Hot melt adhesives, also known as hot glue, are widely used in the automotive industry for various applications due to their versatility, fast curing time, and strong bonding properties. These adhesives are formulated to be solid at room temperature but can be heated to become liquid for application. Once applied, they solidify as they cool down, creating a solid bond between the adhered surfaces. Here are some ways hot melt adhesive is used in the automotive industry:
- Interior Trim Assembly:Hot melt adhesives are commonly used to attach interior components such as fabric, leather, carpeting, and foam to various parts of the vehicle’s interior, including door panels, dashboards, headliners, and seats. The adhesive provides a secure bond, allowing efficient and automated assembly processes.
- Wire Harnesses and Cable Management:Hot melt adhesives secure and protect wire harnesses, cables, and connectors. They help prevent vibration-induced wear and chafing, offer strain relief, and provide insulation against moisture and other environmental factors.
- Sound Dampening and Vibration Control:Hot melt adhesives can dampen sound and reduce vibrations within the vehicle’s interior components. They help improve overall comfort by minimizing noise and vibrations generated by the engine, road, and other sources.
- Weatherstripping and Sealant Applications:Hot melt adhesives are used to attach weatherstrips and seals, helping to create a watertight and airtight seal between various vehicle components. This is crucial for preventing water, air, and dust infiltration, which can affect the vehicle’s performance and passenger comfort.
- Headlights and Taillights:Hot melt adhesives are utilized in assembling automotive lighting components, such as attaching lenses to housings. The adhesive helps seal the elements, preventing moisture and contaminants from entering while ensuring the longevity of the lights.
- Exterior Trim and Emblems:Exterior trims, badges, and emblems are often affixed to the vehicle’s body using hot melt adhesives. These adhesives provide a secure bond and help maintain the vehicle’s aesthetic appearance.
- Acoustic Insulation:Hot melt adhesives are used to attach acoustic insulation materials to the vehicle’s interior panels. This helps reduce noise transmission into the cabin, enhancing passenger comfort.
- Airbag and Safety Component Assembly:Hot melt adhesives play a role in assembling safety components such as airbags and their housings. They help secure these critical components, ensuring proper deployment during a collision.
- Convertible Top Bonding:For convertible vehicles, hot melt adhesives are often used to bond the fabric or vinyl material of the convertible top to the frame, ensuring a secure attachment that withstands the elements.
- Filter and HVAC System Assembly:Hot melt adhesives are employed in assembling air filters and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) components, helping to seal joints and prevent air leaks.
Hot melt adhesives offer benefits such as rapid curing, strong bonds, and resistance to temperature variations in all these applications. They also enable automation in the manufacturing process, leading to increased efficiency and consistency.
What Role Does Hot Melt Adhesive Play in the Textile and Apparel Sector?
Hot melt adhesive (HMA) plays a significant role in the textile and apparel sector, providing a versatile and efficient bonding solution for various applications. Hot melt adhesives are thermoplastic materials that become liquid when heated and solidify upon cooling, creating a solid bond between surfaces. In the textile and apparel industry, HMAs offer several advantages:
- Seam Bonding:HMAs are commonly used in apparel manufacturing to bond seams, hems, and edges of garments. They provide a solid and durable bond without the need for stitching, reducing the bulkiness of seams and enhancing comfort for the wearer.
- Embroidery and Appliqué:Hot melt adhesives attach embroidered patches, appliqués, and embellishments to textiles. They provide a quick and efficient way to add decorative elements to garments without sewing, ensuring a clean and professional finish.
- Label Attachment:HMAs attach labels, tags, and care instructions to garments. This eliminates the need for sewing or pinning, streamlining the labeling process in manufacturing.
- Laminating Fabrics:Textile lamination involves bonding multiple layers of fabric to create composite materials with enhanced properties such as waterproofing, insulation, or reinforcement. HMAs connect these layers without altering the fabric’s appearance or flexibility.
- Seam Sealing and Waterproofing:Hot melt adhesives seal seams and ensure waterproofness in outdoor and performance apparel. These adhesives create a barrier that prevents water penetration, making garments suitable for rainwear, sportswear, and other outdoor applications.
- Bonding Elastic Materials:HMAs are used to attach elastic materials to fabric, which is common in undergarments, swimwear, and activewear. The adhesive provides a flexible yet durable bond that maintains the fabric’s stretchability.
- Textile Repair:Hot melt adhesives are also used for quick repairs on textiles and garments. They can mend small tears and holes without stitching, prolonging the lifespan of clothing items.
- Footwear Manufacturing:In the footwear industry, HMAs are employed to bond various components of shoes, such as attaching soles, insoles, and linings.
- Non-Woven Applications:Non-woven textiles, such as disposable medical gowns, are often assembled using hot melt adhesives. These adhesives allow for efficient bonding without compromising the fabric’s integrity.
The advantages of using hot melt adhesives in the textile and apparel sector include:
- Fast processing times.
- Reduced labor costs.
- Clean aesthetics (no visible stitching).
- The ability to bond various fabrics and materials.
However, it’s essential to consider factors such as the compatibility of the adhesive with different fabrics, the intended use of the garment, and any potential impact on the fabric’s properties before selecting and applying hot melt adhesives.
How Does Hot Melt Adhesive Contribute to the Woodworking and Furniture Industries?
Hot melt adhesive, commonly known as hot glue, is a versatile and widely used adhesive in various industries, including woodworking and furniture. Its contributions to these industries are significant due to its unique properties and ease of use. Here’s how hot melt adhesive contributes to woodworking and furniture:
- Rapid Bonding:Hot melt adhesive is known for its fast-setting properties. It solidifies quickly as it cools, allowing for fast bonding of various woodworking components. This is particularly useful in industries where efficiency and production speed are crucial.
- Versatility:Hot melt adhesive can bond many materials commonly used in woodworking and furniture, including wood, plastic, fabric, foam, and more. This versatility makes it suitable for assembling different components of furniture and woodworking projects.
- Ease of Application:Hot melt adhesive is applied in its molten state, usually using a glue gun. This simple application method requires minimal training, making it accessible to skilled artisans and novices in woodworking and furniture manufacturing.
- No Clamps or Fixtures:Unlike other adhesives that require clamps or fixtures to hold components together until they dry, hot melt adhesive bonds quickly without needing external pressure. This feature helps streamline production processes and reduces the need for additional tools.
- Clean and Neat Bonding:Hot melt adhesive leaves minimal mess or residue behind. The adhesive dries clear and doesn’t create visible lines or marks on the bonded surfaces, essential for maintaining the aesthetic quality of furniture and woodwork.
- Temperature Resistance:While hot melt adhesive can soften at high temperatures, it retains its bonding strength under normal indoor conditions. This makes it suitable for applications in furniture that might be exposed to varying temperatures.
- Repair and Assembly:Hot melt adhesive is often used in woodworking for repair and assembly. It can quickly fix loose joints, reattach small parts, and mend minor damages, allowing for efficient repairs in furniture manufacturing and woodwork projects.
- Cost-Efficiency:Hot melt adhesive systems are relatively cost-effective compared to other options. The adhesive is affordable, and the simplified application reduces labor and equipment costs.
- Customization:With various formulations available, hot melt adhesives can be tailored to specific woodworking and furniture requirements. Different formulations can provide varying bonding strength, flexibility, and durability levels.
- Environmental Benefits:Many hot melt adhesive formulations are solvent-free, making them more environmentally friendly than solvent-based adhesives. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the woodworking and furniture industries.
What Are the Environmental Considerations for Hot Melt Adhesive?
Hot melt adhesives, also known as hot glue, are widely used in various industries for bonding applications due to their quick-setting and strong adhesive properties. However, several critical environmental considerations are associated with using hot melt adhesives. These considerations include:
- Emission of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):Some hot melt adhesives can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air during the application process and as they cure. VOCs can contribute to air pollution and adversely affect air quality and human health.
- Energy Consumption:Applying hot melt adhesives requires heating the adhesive to a specific temperature. This heating process consumes energy, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and increase the carbon footprint of a manufacturing process.
- Waste Generation:Packaging materials, such as plastic cartridges or containers used to hold hot melt adhesives, can generate waste that adds to the overall environmental impact. Proper disposal and recycling of these materials are essential to minimize waste.
- End-of-Life Disposal:When products bonded with hot melt adhesives reach the end of their useful life, the adhesive can complicate recycling processes. The adhesive may need to be removed before recycling, which can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Resource Consumption:The production of hot melt adhesives requires raw materials, energy, and water. The sourcing and extracting of these resources can have environmental implications, including habitat destruction and resource depletion.
- Packaging:Packaging hot melt adhesive products should be considered from an environmental perspective. Using sustainable and recyclable packaging materials can reduce the overall environmental impact.
- Temperature Sensitivity:Hot melt adhesives are applied at elevated temperatures. This can impact the immediate environment in terms of heat generation and may also affect the adhesive’s performance in applications where temperature changes are a concern.
- Health and Safety:While hot melt adhesives are generally considered safe to use when handled properly, there can be health and safety considerations for workers exposed to the adhesive’s fumes, high temperatures, and potential burns.
To mitigate these environmental considerations, manufacturers and users of hot melt adhesives can take several actions:
- Formulation Improvements:Develop adhesives with lower VOC emissions and reduced environmental impact.
- Efficient Application:Optimize application processes to minimize energy consumption and reduce adhesive waste.
- Recycling and Disposal:Explore methods for recycling bonded products and disposing of adhesive waste responsibly.
- Sustainable Sourcing:Source raw materials from sustainable and environmentally responsible suppliers.
- Education and Training:Provide proper training to workers on safe handling, application techniques, and use of personal protective equipment.
Companies and users need to assess the environmental impact of their adhesive choices and consider using more sustainable alternatives when feasible. Additionally, regulatory compliance and best practices should be followed to minimize the adverse environmental effects of hot melt adhesive use.
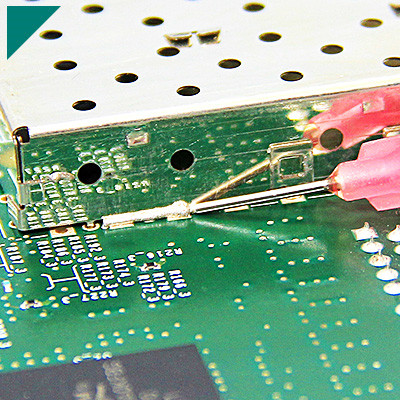
How Is Hot Melt Adhesive Utilized in Electronics Manufacturing?
Hot Melt Adhesive (HMA), also known as hot glue, is used in various applications within electronics manufacturing due to its versatility, ease of use, and fast-setting properties. Here are some ways in which hot melt adhesive is utilized in electronics manufacturing:
- Cable Management:Hot melt adhesive is commonly used to secure and manage cables within electronic devices, preventing tangling and providing strain relief. It’s applied to secure cables to PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) and other components, ensuring proper routing and organization.

2.Component Bonding:Hot melt adhesive can bond electronic components onto circuit boards. It provides a robust and quick bond that helps secure parts in place during assembly. This is especially useful for temporary placement before permanent soldering or in cases where soldering might not be suitable.
3.Sealing and Encapsulation:HMAs can create a protective barrier around sensitive electronic components, shielding them from moisture, dust, and other contaminants. This is particularly important for parts exposed to harsh environments or outdoor conditions.
Potting involves encapsulating sensitive electronic components in a protective shell of hot melt adhesive. This helps enhance the durability and longevity of the pieces, making them more resistant to vibration, shock, and environmental stress.
4.Wire Tacking:In some cases, wires or leads need to be temporarily held in place during assembly. Hot melt adhesive can be applied to secure these wires and easily removed later without damaging the components.
5.Bonding Enclosures:Hot melt adhesive is used to secure enclosure components like panels, covers, and bezels in place. It can create a strong bond while also allowing for disassembly if needed.
6.Quick Repairs:Hot melt adhesive can be used for fast, temporary repairs in electronics manufacturing. If a component becomes loose or detached during assembly, hot melt adhesive can secure it temporarily until a more permanent solution can be applied.
7.Solder Masking:During the soldering process, hot melt adhesive can mask off areas of a PCB where solder should not be applied. This prevents solder from bridging connections or contaminating sensitive areas.
8.Sensor Mounting:In applications involving sensors or detectors, hot melt adhesive can securely attach these components to various surfaces or housings.
9.Connector Stabilization:HMAs can be used to secure connectors and sockets in place on PCBs or within electronic devices. This ensures that connectors remain stable even in frequent plugging and unplugging situations.
It’s important to note that while hot melt adhesive offers many advantages, it may only be suitable for some electronics manufacturing applications. Factors such as operating temperature, material compatibility, and the specific requirements of the electronic components should be considered when choosing the appropriate adhesive for a particular task.
What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Working with Hot Melt Adhesive?
Working with hot melt adhesive (also known as hot glue) can pose risks due to its high temperature and adhesive properties. To ensure your safety, consider the following precautions:
- Protective Clothing and Gear:
- Wear appropriate clothing to cover exposed skin and avoid direct contact with hot adhesive.
- Use heat-resistant gloves to protect your hands from burns.
- Eye Protection:
- Wear safety goggles or glasses to prevent accidental splashes of hot adhesive from coming into contact with your eyes.
- Ventilation:
- Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of fumes released during the melting process.
- Temperature Control:
- Ensure the hot melt adhesive equipment is calibrated correctly to maintain a consistent and safe temperature.
- Avoid overheating the adhesive, as it can release potentially harmful fumes or cause the adhesive to break down.
- Fire Safety:
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby, mainly if you use hot melt adhesive near flammable materials.
- Avoid open flames or ignition sources in the vicinity of the adhesive.
- Proper Workspace Setup:
- Clear the workspace of any clutter or items that could be accidentally knocked into the adhesive or heating equipment.
- Preventing Contact with Hot Adhesive:
- Handle hot melt adhesive guns and tools carefully, and avoid touching the heated surfaces.
- Keep fingers and body parts away from the adhesive stream during application.
- Cooling Time:
- Allow the adhesive to cool and set appropriately before handling or moving the bonded materials.
- Storage and Handling of Adhesive Sticks:
- Store adhesive sticks in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper storage and handling of adhesive sticks.
- Training and Education:
- Ensure that anyone working with hot melt adhesive is adequately trained in its safe usage and is aware of potential hazards.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- Know the location of emergency exits, first aid kits, and other safety equipment in case of accidents.
- Read Manufacturer’s Instructions:
- Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for your specific adhesive.
Remember that different adhesives and equipment may have specific safety considerations, so it’s essential to refer to the product’s safety data sheet (SDS) and the manufacturer’s instructions for accurate information tailored to your specific situation.
How Is Hot Melt Adhesive Applied in the Bookbinding and Paper Converting Processes?
Hot melt adhesive, also known as hot glue, is commonly used in the bookbinding and paper-converting processes due to its fast bonding properties and versatility. It is applied in various forms to bind pages, secure packaging, and assemble paper products. Here’s how hot melt adhesive is typically used in these processes:
Bookbinding Process:
Perfect Binding:This is the process used to create paperback books. In perfect binding, hot melt adhesive is applied to the spine of the book block (the stack of pages) in the form of a continuous, thin line.
-
- Application:Hot melt adhesive is applied using a perfect binder machine. The adhesive is melted and involved in a precise line along the spine of the book block.
- Curing:Once the adhesive is applied, the cover is pressed onto the spine, and the adhesive quickly cools and solidifies, creating a solid bond.
- Saddle Stitching:Saddle stitching is used for smaller booklets or magazines with fewer pages. In this process, hot melt adhesive is often used to strengthen the spine.
- Application:A machine applies a thin line of hot melt adhesive to the booklet’s spine before folding and stapling the pages together.
Paper Converting Process:
Packaging:Hot melt adhesive is widely used for sealing cardboard boxes, attaching labels, and securing other packaging materials.
-
- Application:Automated machines apply hot melt adhesive in specific patterns, such as dots or lines, to bond various parts of the packaging material.
- Folding and Gluing:Hot melt adhesive is used to fold and glue paper products like envelopes, folders, and cartons.
- Application:The adhesive is applied in precise patterns on the flaps or edges of the paper product. Machines then fold and press the adhesive-coated areas to create a secure bond.
- Laminating:Hot melt adhesive is used to bond layers of paper or cardboard to create laminated products with enhanced strength and durability.
- Application:The adhesive is applied in a controlled pattern between the layers of material, and pressure is applied to ensure proper bonding.
Hot melt adhesive application machines are designed to ensure accurate and consistent adhesive placement, and they often have features to control adhesive temperature and application speed. The adhesive’s fast bonding properties are advantageous because they allow efficient production with minimal drying or curing time.
It’s important to note that various types of hot melt adhesives are available, each with different formulations and properties suited for specific applications. Manufacturers choose the appropriate adhesive based on factors such as the type of paper, the environment in which the product will be used, and the required bond strength.
What Challenges and Limitations Are Associated with Hot Melt Adhesive?
While versatile and widely used in various industries, hot melt adhesives come with their own challenges and limitations. Here are some of the key challenges and constraints associated with hot melt adhesives:
- Temperature Sensitivity:Hot melt adhesives require elevated temperatures for application, which can limit their use with heat-sensitive materials. High temperatures can cause damage or distortion to delicate substrates.
- Limited Heat Resistance:Hot melt adhesives generally have lower heat resistance than other adhesive types. They can soften and lose their adhesive properties at higher temperatures, which can be a concern in applications where the bonded materials will be exposed to heat.
- Lack of Structural Strength:Compared to other adhesive types, hot melt adhesives might provide a different level of structural strength. They are better suited for bonding lightweight materials and providing temporary or semi-permanent bonds.
- Limited Chemical Resistance:Hot melt adhesives might not hold up well against exposure to certain chemicals or solvents. They can soften or degrade when in contact with certain substances, limiting their use in applications where chemical resistance is essential.
- Quick Setting Time:The rapid cooling and setting of hot melt adhesives can be a limitation in some scenarios. Once applied, they solidify quickly, allowing a little time to reposition or align parts before forming the bond.
- Limited Bonding Substrates:Hot melt adhesives might only bond effectively to some substrates. They work best on porous surfaces, and their performance can be compromised when connecting non-porous or low-energy surfaces like certain plastics.
- Environmental Concerns:Some hot melt adhesives are made from synthetic petrochemical polymers. This raises concerns about their environmental impact and sustainability. However, efforts are being made to develop more eco-friendly alternatives.
- Cold Weather Performance:In colder environments, hot melt adhesives can become brittle and lose their flexibility, potentially affecting the integrity of the bond. This limitation can be problematic in applications that are exposed to varying temperatures.
- Storage and Shelf Life:Hot melt adhesives can have a limited shelf life, especially if exposed to temperature fluctuations. Over time, they might lose their adhesive properties or change in consistency, affecting their usability.
- Noise and Odor:Hot melt adhesives can produce noise and odor during application due to heating. This can be a concern in applications where a quiet and odor-free environment is essential.
Despite these challenges and limitations, hot melt adhesives remain popular for their fast application, versatility, and cost-effectiveness in various industries. It’s essential to carefully consider these limitations and select the right adhesive type for the specific application to ensure optimal performance and durability.
How Can Hot Melt Adhesive Enhance Product Assembly in Various Sectors?
Hot melt adhesive, or hot glue, is a thermoplastic adhesive that is melted and applied in a liquid state to bond various materials. It offers several advantages that can enhance product assembly in multiple sectors. Here’s how hot melt adhesive can be beneficial in different industries:
- Packaging Industry:
- Carton sealing: Hot melt adhesive provides a quick and secure bond for sealing cartons, boxes, and packages. It offers high initial tack and fast setting, which increases packaging efficiency on production lines.
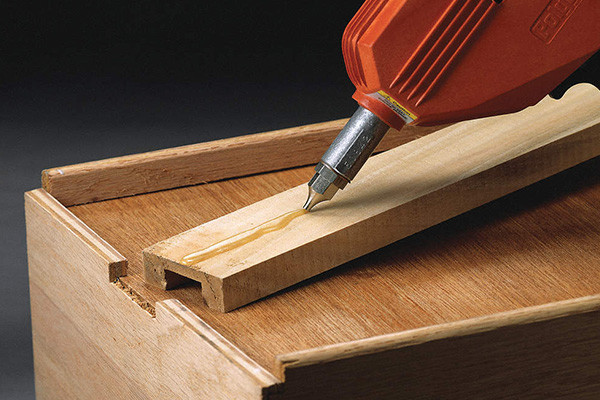

2.Tamper-evident seals: Hot melt adhesives can create tamper-evident seals that are difficult to break without leaving visible evidence, enhancing the security of packaged goods.
3.Labeling: Hot melt adhesives are used for labeling applications, ensuring labels adhere firmly to various substrates and maintaining label integrity during shipping and handling.
2.Automotive Industry:
Interior assembly: Hot melt adhesives bond fabrics, foams, and other interior materials in vehicles. They provide vibration damping, noise reduction, and flexibility in the community.
Exterior components: Hot melt adhesives are used in bonding trim, badges, and other external elements, replacing mechanical fasteners and improving aesthetics.
3.Electronics Industry:
Component bonding: Hot melt adhesives attach components in electronics assemblies. They offer good electrical insulation, shock absorption, and heat dissipation.
Cable and wire management: Hot melt adhesives are employed to secure and insulate cables, wires, and connectors in electronics products.
4.Textile and Apparel Industry:
Fabric bonding: Hot melt adhesives can bond fabrics without stitching, creating seamless garments and textiles.
Embellishments: Hot melt adhesives attach embellishments like rhinestones, sequins, and appliqués to clothing items.
5.Woodworking Industry:
Edgebanding: Hot melt adhesives are applied to the edges of wooden panels to bond edge banding tapes, creating a seamless and durable finish.
Assembly and joinery: Hot melt adhesives provide a quick and strong bond for assembling wooden components, reducing the need for traditional nails and screws.
6.Food and Beverage Industry:
Packaging: Hot melt adhesives are used for sealing food and beverage packaging, ensuring a hygienic and secure seal that withstands temperature variations.
Labeling: Hot melt adhesives are suitable for adhering labels to food packaging, as they are FDA-approved and food-safe.
7.Medical Industry:
Device assembly: Hot melt adhesives are used in medical device assembly due to their biocompatibility, sterilization resistance, and ability to bond various medical-grade materials.
Wound dressings: Hot melt adhesives can be used in medical sauces to adhere securely to the skin, allowing easy removal.
In all these sectors, hot melt adhesive offers advantages such as rapid bonding, versatility in materials, reduced need for mechanical fasteners, improved aesthetics, and enhanced production efficiency. However, it’s essential to consider factors like material compatibility, temperature resistance, and application techniques when selecting the appropriate hot melt adhesive for specific assembly needs.
What Are the Future Trends and Innovations in Hot Melt Adhesive Technology?
Hot melt adhesive technology is continuously advancing and is poised to shape various industries in the coming years. Some of the notable future trends and innovations in this field include:
- Sustainability and Eco-friendliness: The hot melt adhesive industry is moving towards more environmentally friendly formulations. Researchers are developing bio-based and renewable feedstock options, reducing the dependency on fossil fuels. Manufacturers strive to create adhesive products with lower carbon footprints and reduced emissions during production and application.
- Innovative Adhesives: Integrating intelligent technologies into hot melt adhesives is on the horizon. These adhesives can respond to environmental changes like temperature, humidity, or pressure. They have the potential to be used in various applications, such as sensors, wearable electronics, and healthcare devices.
- Nanotechnology and Enhanced Performance: Researchers are exploring nanomaterials to improve the performance of hot melt adhesives. Nano additives can enhance adhesive properties, such as bonding strength, heat resistance, and durability. This innovation opens up opportunities for using hot melt adhesives in more demanding applications, including the aerospace and automotive industries.
- Customization and 3D Printing: Hot melt adhesive technology will likely integrate with 3D printing techniques. This combination allows for the precise deposition of adhesives in intricate patterns, enabling customization and rapid prototyping across manufacturing, electronics, and healthcare industries.
- Improved Application Techniques: Innovations in application methods are expected, leading to more efficient and precise adhesive deposition. These advancements include robotic systems, automated dispensing, and nozzle designs that optimize adhesive distribution while minimizing waste.
- Healthcare and Biomedical Applications: Hot melt adhesives are being explored for medical devices and wound care applications. Developing biocompatible and biodegradable adhesive formulations could revolutionize medical procedures and patient care.
- High-Temperature Applications: Adhesives capable of withstanding extreme temperatures are gaining attention. These adhesives can be used in industries like automotive and electronics, where exposure to heat and thermal cycling is every day.
- Packaging and E-Commerce: The packaging industry is adopting hot melt adhesives for their versatility and fast curing times. With the growth of e-commerce, there’s a demand for adhesives that offer strong bonds for various packaging materials while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
- Adhesives for Flexible Electronics: As the demand for flexible electronic devices grows, hot melt adhesives are being developed to adhere to various substrates while maintaining flexibility and conductivity.
- Cross-Industry Collaboration: Future innovation in hot melt adhesive technology is likely to be driven by cross-industry collaboration. Experts from various fields, such as chemistry, engineering, and materials science, will collaborate to create adhesive solutions that cater to specific industry needs.
In summary, the future of hot melt adhesive technology is characterized by sustainability, customization, advanced materials, and integration with emerging technologies. These trends are expected to transform various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to electronics.