Silicone-Based Fireproof Glue Suitable for Construction/Electronic Scenarios
Silicone-Based Fireproof Glue Suitable for Construction/Electronic Scenarios
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the need for materials that prioritize safety, durability, and versatility has never been more critical. Silicone-based fireproof glue emerges as a standout solution, particularly tailored for demanding environments in construction and electronics. This adhesive, engineered from silicone polymers infused with flame-retardant additives, offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures, flames, and environmental stressors. Unlike traditional adhesives that may degrade or ignite under heat, silicone-based variants form a protective barrier, maintaining structural integrity and preventing fire propagation. This makes them indispensable in scenarios where fire hazards are prevalent, such as building facades, electrical enclosures, and circuit assemblies.
The construction industry, with its emphasis on fire-rated structures, benefits immensely from this glue’s ability to seal joints, bond insulation, and enhance overall fire resistance. In electronics, where miniaturization and heat management are key, it provides insulation, vibration damping, and thermal stability, safeguarding sensitive components from overheating or short circuits.
Global standards like UL 94 for flammability and ASTM E84 for surface burning underscore the importance of such materials, driving their adoption amid stricter regulations post-incidents like the Grenfell Tower fire. At its essence, silicone-based fireproof glue is composed of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) chains, enhanced with fillers like aluminum trihydroxide (ATH) or magnesium hydroxide to achieve low smoke emission and self-extinguishing properties.
These formulations not only bond diverse substrates—metals, plastics, glass, and wood—but also withstand temperatures up to 300°C or more, making them ideal for both sectors. As industries shift toward sustainable practices, these glues stand out for their low volatile organic compound (VOC) content and recyclability potential, reducing environmental impact while enhancing safety.
This article explores the history, science, properties, and targeted applications of silicone-based fireproof glue in construction and electronics. Through case studies and discussions on challenges, it highlights how this innovative adhesive is revolutionizing safety protocols, ensuring resilience in high-stakes scenarios.
 History and Development
History and Development
The origins of silicone-based adhesives date back to the 1940s, when silicones were first commercialized by pioneers like Frederick Kipping and later refined by companies such as Dow Corning. Initially developed for military applications during World War II, silicones were valued for their thermal stability and electrical insulation, used in aircraft seals and radar components.
The transition to fire-retardant variants gained momentum in the 1960s and 1970s, spurred by industrial fires and the need for safer materials in burgeoning electronics and construction sectors. By the 1980s, environmental concerns led to the phasing out of halogenated flame retardants, prompting innovations in silicone matrices. Researchers incorporated inorganic fillers to enhance flame retardancy without toxic byproducts. A pivotal development was the introduction of room-temperature vulcanizing (RTV) silicones, which cured without heat, facilitating easier application in construction sites and electronic assembly lines.
The 1990s saw advancements in nanotechnology, with additions like silica nanoparticles improving adhesion and heat resistance. Collaborative efforts between academia and industry, such as those at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), tested these adhesives in fire simulations, leading to formulations compliant with international standards. In electronics, the rise of consumer devices necessitated glues that could handle miniaturization, resulting in low-outgassing variants for circuit protection.
Entering the 2000s, sustainability drove further evolution. Bio-based silicones and hybrid systems combining silicones with epoxies emerged, offering enhanced mechanical properties. Recent developments, as of 2025, include smart adhesives with self-healing capabilities, integrating sensors for real-time fire detection in smart buildings and IoT devices. The history reflects a trajectory from basic sealants to sophisticated, multi-functional glues, driven by safety demands and technological progress.
The Science Behind Silicone-Based Fireproof Glue
The efficacy of silicone-based fireproof glue stems from its unique molecular structure. Silicones feature a backbone of alternating silicon-oxygen atoms, providing inherent flexibility and thermal resistance far superior to carbon-based polymers. When exposed to fire, the glue undergoes a controlled degradation, forming a silica-rich char layer that acts as an insulating barrier, reducing heat transfer and oxygen ingress.
Flame retardancy is bolstered by additives like ATH, which decomposes endothermically, absorbing heat and releasing water vapor to dilute flammable gases. In intumescent formulations, the adhesive expands upon heating, creating a foamy char that further impedes flame spread. For electronics, low-thermal-conductivity variants incorporate ceramic fillers to manage heat dissipation without compromising electrical insulation.
Chemically, the curing process—often via hydrosilylation or condensation—ensures strong cross-linking, yielding a rubber-like elastomer resistant to cracking under thermal cycling. Studies using cone calorimetry reveal that these glues exhibit low peak heat release rates (PHRR), often below 100 kW/m², compared to 200+ for untreated adhesives. This scientific foundation enables tailored formulations: neutral-cure for construction to avoid corrosion, and fast-cure for high-throughput electronics assembly.
Properties and Benefits
Silicone-based fireproof glue boasts a suite of properties that make it superior for construction and electronics. Key among them is high-temperature resistance, enduring up to 300°C continuously and peaks of 500°C, without losing adhesion. Its flexibility, with elongation over 300%, accommodates substrate movement, preventing failures in seismic-prone buildings or vibrating electronic devices.
Benefits include excellent weatherability, resisting UV, ozone, and moisture, which extends service life in outdoor construction applications. In electronics, high dielectric strength (up to 500 V/mil) ensures insulation, while low toxicity and minimal smoke generation enhance safety during fires. Compared to epoxies, silicones offer better thermal shock resistance, reducing delamination risks. Economically, their durability minimizes maintenance, and ease of application—via cartridges or sprays—speeds up processes. Environmentally, halogen-free compositions align with RoHS directives, promoting green building and electronics manufacturing.
Applications in Construction
In construction, silicone-based fireproof glue is pivotal for enhancing building safety. It seals expansion joints in fire-rated walls, preventing smoke and flame penetration for up to two hours, as per EN 1366 standards. For glazing, it bonds fire-resistant glass in doors and partitions, maintaining integrity under intense heat.
In plywood and composite bonding, it acts as a flame-retardant layer, suppressing smoldering and reducing heat release by 20-30%. High-rise structures utilize it for facade sealing, where its UV resistance ensures long-term performance against weathering. In HVAC systems, it seals ducts to contain fire spread, while in roofing, it bonds membranes for waterproof, fireproof barriers.
Its low-modulus nature allows for movement in earthquake zones, making it suitable for modern modular construction. Overall, it contributes to LEED-certified buildings by improving energy efficiency through airtight seals.
Applications in Electronics
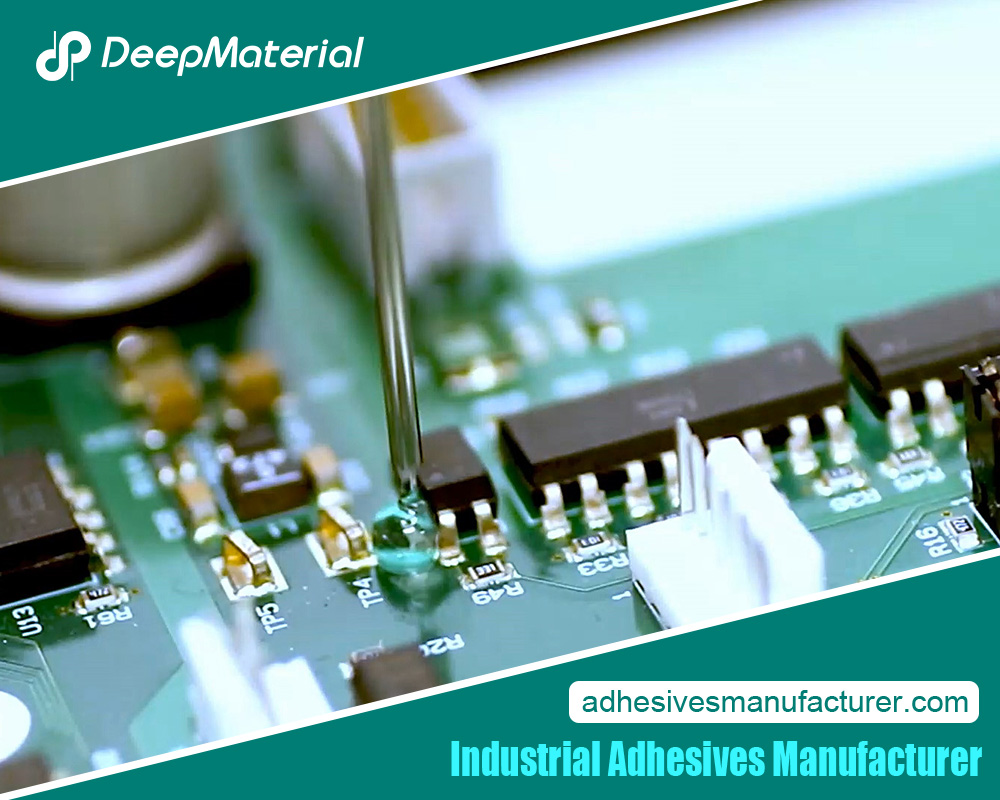
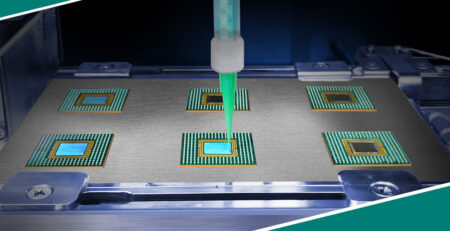
Electronics demand precision and reliability, where silicone-based fireproof glue excels in potting, encapsulation, and conformal coatings. It protects circuit boards from moisture, dust, and thermal shocks, with formulations like RTV silicones curing quickly for mass production.
In LED lighting, it bonds components while dissipating heat, extending lifespan. For automotive electronics, it seals sensors against engine heat, meeting AEC-Q100 standards. In consumer devices, it provides vibration damping in smartphones and wearables, preventing failures.
Thermally conductive variants aid in heat sinks, while flame-retardant grades ensure compliance with UL 94 V-0 ratings in power supplies. Emerging uses include EV batteries, where it insulates cells to prevent thermal runaway.
Case Studies
A case in plywood manufacturing demonstrated silicone adhesive reducing combustion risks, forming protective layers that suppressed glowing. In electronics, a sensor assembly study showed enhanced durability under heat, per peer-reviewed patents. Construction examples include fire-sealant use in high-rises, improving evacuation times.
Challenges and Future Trends
Challenges include higher costs and slower curing in humid environments. Future trends involve nanocomposites for strength and AI-integrated formulations for predictive maintenance.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Silicone-based fireproof glue is transforming safety in construction and electronics, offering unmatched protection and versatility. Its continued evolution promises even greater innovations.
For more about silicone-based fireproof glue suitable for construction/electronic scenarios, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.